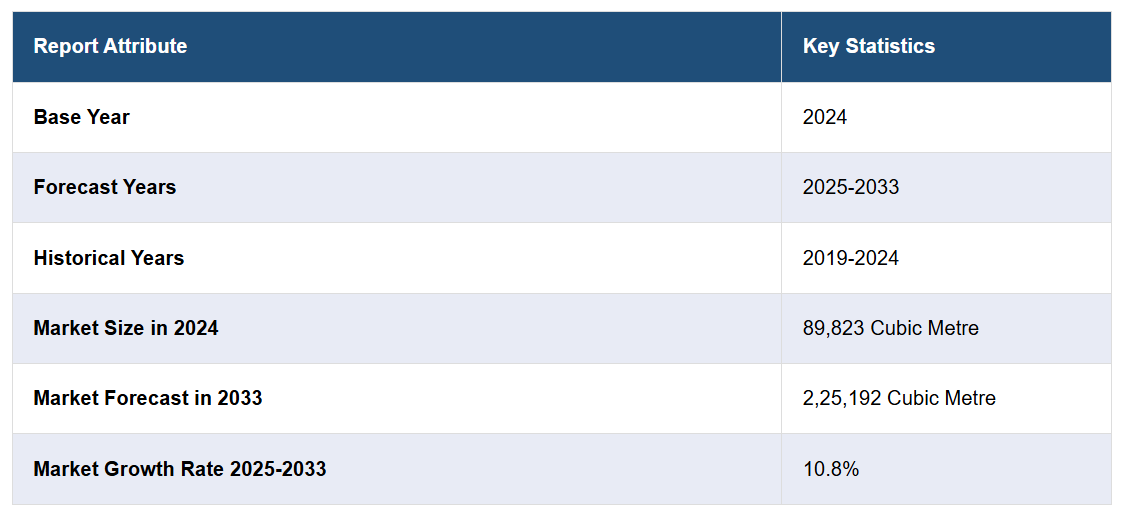
The Japan cross laminated timber (CLT) market size reached 89,823 Cubic Metre in 2024. Looking forward, IMARC Group expects the market to reach 2,25,192 Cubic Metre by 2033, exhibiting a growth rate (CAGR) of 10.8% during 2025-2033.
The Japan Cross-Laminated Timber (CLT) market is witnessing a significant transformation, reflecting the nation’s broader transition toward sustainability in architecture and construction. Traditionally reliant on concrete and steel-based construction, Japan is increasingly adopting eco-friendly and renewable materials, with CLT emerging as a frontrunner due to its multifaceted advantages, structural versatility, and strong alignment with the country’s environmental policies and construction needs.
CLT, a form of engineered wood constructed by layering and gluing timber planks at perpendicular angles, offers a wide array of benefits—lightweight structure, high load-bearing strength, seismic resilience, thermal insulation, fire resistance, and design flexibility. These characteristics make it highly attractive for modern construction applications ranging from residential buildings to large-scale public infrastructure. Unlike traditional Japanese wooden architecture, which relies on post-and-beam systems, CLT uses a larger volume of timber and allows for more robust and scalable structural solutions, opening the door to multi-story wooden buildings, including four-story or taller commercial and institutional structures that were previously limited to non-timber materials.
Government Support and Policy Frameworks Fueling Market Expansion
A pivotal factor driving the adoption of CLT in Japan is the active involvement of the Japanese government, which is spearheading various legislative and financial initiatives to promote wood-based construction. One of the most impactful regulatory measures was the enactment of the “Promotion of Use of Wood in Public Buildings Act” in 2010, mandating the use of wood in government buildings up to three stories high. This policy move has laid the groundwork for a surge in CLT adoption within public sector construction projects, creating a solid foundation for broader market development.
Further reinforcing this trajectory, the Japanese Forest Agency has been tasked with developing a national roadmap for CLT utilization, including financial subsidies for manufacturing facilities, research support, and logistical development. These efforts aim to expand domestic CLT production capacity, ensuring Japan not only meets internal demand but also establishes itself as a key player in the global CLT export market.
Japan’s unique geological profile also contributes to this shift. Given its location at the convergence of four tectonic plates, the country faces frequent earthquake activity. CLT has proven to be exceptionally resilient to seismic forces, offering better performance under stress compared to traditional materials like concrete. This seismic resistance, along with CLT’s ability to reduce construction weight and improve flexibility, has become a critical selling point for its application in earthquake-prone urban zones.
Applications Driving CLT Market Penetration
The Japan CLT market is categorized by application into four primary segments: Residential Construction, Government/Public Buildings, Commercial Buildings, and Educational Institutions.
-
Residential Sector:
Increasing interest in sustainable living, coupled with the push for energy-efficient housing solutions, is boosting CLT usage in urban and rural residential projects. Homeowners are recognizing the thermal insulation and acoustic properties of CLT, along with its reduced construction time and aesthetic appeal. As eco-consciousness continues to grow among Japanese consumers, CLT is becoming a preferred material in new residential developments and green building projects. -
Government and Public Infrastructure:
This segment plays a pivotal role in CLT market growth, thanks to the aforementioned legislative mandates promoting wood-based public construction. CLT is being incorporated into municipal offices, community centers, fire stations, and other public service buildings. These projects not only demonstrate the structural capabilities of CLT but also serve as public endorsements of its performance and sustainability. -
Commercial Buildings:
With the rise of sustainable commercial architecture, many developers are turning to CLT for office complexes, retail spaces, and hospitality properties. CLT enables efficient modular construction, reduces carbon footprint, and delivers superior design aesthetics. This combination of benefits appeals to modern businesses seeking to integrate corporate sustainability objectives into their physical infrastructure. -
Educational Institutions:
Schools and universities are increasingly integrating CLT in their campus infrastructure, valuing the natural material’s warmth, durability, and indoor air quality benefits. Additionally, the reduced noise levels and eco-friendly characteristics of CLT buildings create optimal learning environments. Government support for low-carbon public buildings further encourages the expansion of CLT in the educational sector.
Market Landscape and Key Players
The competitive environment in the Japan CLT market remains relatively concentrated, with a limited number of manufacturers currently dominating the supply chain. However, these players are distinguished by their product quality, pricing strategies, and technological capabilities, positioning themselves to capitalize on growing demand. Leading companies in this space include:
-
Meiken Lamwood Corporation
-
Middle East Co. Ltd.
-
Yamasa Mokuzai Co. Ltd.
These companies are actively investing in production capacity expansion, automation technologies, and R&D efforts to improve CLT performance and affordability. Their strategic focus includes developing tailored CLT solutions for diverse construction applications and exploring international markets through export initiatives.
Challenges and Emerging Opportunities
While the market shows promising growth, there are also certain challenges to be addressed, including:
-
High initial costs of CLT compared to conventional materials.
-
Lack of skilled labor experienced in timber construction techniques.
-
Regulatory barriers regarding fire codes and structural design standards for high-rise wooden buildings.
Nevertheless, these obstacles are being mitigated through government incentives, public-private partnerships, and educational programs that promote timber construction skills. Furthermore, as construction companies become more familiar with CLT technologies, the cost-effectiveness and value proposition of these materials are expected to improve over time.
At the same time, export opportunities, green building certifications, and urban sustainability goals continue to drive market innovation. Demand for carbon-sequestering materials, along with increasing interest in modular and prefabricated construction, positions CLT as a critical material for the future of global architecture.
Conclusion and Strategic Outlook
The Japan cross laminated timber market is evolving into a vital component of the country’s green building strategy. Driven by regulatory backing, environmental responsibility, seismic resilience, and superior performance attributes, CLT is becoming a core material across various construction segments. With anticipated growth between 2025 and 2033, supported by strong institutional frameworks and rising industry awareness, the market is set to expand further and redefine conventional building practices in Japan.
Who Should Read This Report?
This report is an essential resource for:
-
Real estate developers and architects seeking sustainable materials.
-
Timber and construction material manufacturers.
-
Government policy advisors and urban planners.
-
Investors and stakeholders evaluating green construction markets.
-
Consultants, engineers, and building contractors involved in structural design and sustainable construction practices.
Table of Contents
1 Preface
2 Scope and Methodology
2.1 Objectives of the Study
2.2 Stakeholders
2.3 Data Sources
2.3.1 Primary Sources
2.3.2 Secondary Sources
2.4 Market Estimation
2.4.1 Bottom-Up Approach
2.4.2 Top-Down Approach
2.5 Forecasting Methodology
3 Executive Summary
4 Introduction
4.1 Overview
4.2 Key Industry Trends
5 Global Cross Laminated Timber Industry
5.1 Market Overview
5.2 Market Performance
5.2.1 Volume Trends
5.2.2 Value Trends
5.3 Market Breakup by Application
5.4 Market Forecast
6 Japan Cross Laminated Timber Industry
6.1 Market Overview
6.2 Market Performance
6.2.1 Volume Trends
6.2.2 Value Trends
6.3 Impact of COVID-19
6.4 Price Analysis
6.4.1 Key Price Indicators
6.4.2 Price Structure
6.4.3 Price Trends
6.5 Market Breakup by Application
6.6 Market Forecast
6.7 SWOT Analysis
6.7.1 Overview
6.7.2 Strengths
6.7.3 Weaknesses
6.7.4 Opportunities
6.7.5 Threats
6.8 Value Chain Analysis
6.8.1 Overview
6.8.2 Research and Development
6.8.3 Raw Material Procurement
6.8.4 Manufacturing
6.8.5 Marketing
6.8.6 Distribution
6.8.7 End-Use
6.9 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
6.9.1 Overview
6.9.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers
6.9.3 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
6.9.4 Degree of Competition
6.9.5 Threat of New Entrants
6.9.6 Threat of Substitutes
6.10 Key Drivers and Success Factors
7 Market Breakup by Application
7.1 Residential
7.1.1 Market Trends
7.1.2 Market Forecast
7.2 Government/Public Buildings
7.2.1 Market Trends
7.2.2 Market Forecast
7.3 Commercial Buildings
7.3.1 Market Trends
7.3.2 Market Forecast
7.4 Educational Institutes
7.4.1 Market Trends
7.4.2 Market Forecast
8 Cross Laminated Timber Environmental Impact/Benefit Analysis
9 Cross Laminated Timber Financial Impact/Benefit Analysis
10 Japan-Codes and Standards
11 Japan-Pilot Projects
12 Competitive Landscape
12.1 Competitive Structure
12.2 Key Players
13 Cross Laminated Timber Manufacturing Process
13.1 Product Overview
13.2 Detailed Process Flow
13.3 Various Types of Unit Operations Involved
13.4 Mass Balance and Raw Material Requirements
14 Requirements for Setting Up a Cross Laminated Timber Manufacturing Plant
14.1 Land Requirements
14.2 Construction Requirements
14.3 Plant Layout
14.4 Plant Machinery
14.5 Machinery Pictures
14.6 Raw Material Requirements
14.7 Raw Material and Final Product Pictures
14.8 Packaging Requirements
14.9 Transportation Requirements
14.10 Utility Requirements
14.11 Manpower Requirements
15 Profiles of Key Players
15.1 Meiken Lamwood Corporation
15.2 Middle East Co. Ltd.
15.3 Yamasa Mokuzai Co. Ltd.
List of Figures
Figure 1: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Market: Major Drivers and Challenges
Figure 2: Global: Cross Laminated Timber Market: Volume Trends (in Cubic Metre), 2019-2024
Figure 3: Global: Cross Laminated Timber Market: Value Trends (in Million USD), 2019-2024
Figure 4: Global: Cross Laminated Timber Market: Breakup by Application (in %), 2024
Figure 5: Global: Cross Laminated Timber Market Forecast: Volume Trends (in Cubic Metre), 2025-2033
Figure 6: Global: Cross Laminated Timber Market Forecast: Value Trends (in Million USD), 2025-2033
Figure 7: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Market: Volume Trends (in Cubic Metre), 2019-2024
Figure 8: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Market: Value Trends (in Million USD), 2019-2024
Figure 9: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Market: Average Prices (in USD/cubic Meter), 2019-2033
Figure 10: Cross Laminated Timber: Price Structure
Figure 11: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Market: Breakup by Application (in %), 2024
Figure 12: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Market Forecast: Volume Trends (in Cubic Metre), 2025-2033
Figure 13: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Market Forecast: Value Trends (in Million USD), 2025-2033
Figure 14: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Industry: SWOT Analysis
Figure 15: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Industry: Value Chain Analysis
Figure 16: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Industry: Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
Figure 17: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Market (in Residential Applications): Volume Trends (in Cubic Metre), 2019 & 2024
Figure 18: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Market Forecast (in Residential Applications): Volume Trends (in Cubic Metre), 2025-2033
Figure 19: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Market (in Government/Public Buildings Applications): Volume Trends (in Cubic Metre), 2019 & 2024
Figure 20: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Market Forecast (in Government/Public Buildings Applications): Volume Trends (in Cubic Metre), 2025-2033
Figure 21: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Market (in Commercial Building Applications): Volume Trends (in Cubic Metre), 2019 & 2024
Figure 22: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Market Forecast (in Commercial Building Applications): Volume Trends (in Cubic Metre), 2025-2033
Figure 23: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Market (in Educational Institute Applications): Volume Trends (in Cubic Metre), 2019 & 2024
Figure 24: Japan: Cross Laminated Timber Market Forecast (in Educational Institute Applications): Volume Trends (in Cubic Metre), 2025-2033
Figure 25: CLT Manufacturing Plant: Detailed Process Flow
Figure 26: CLT Manufacturing: Conversion Rate of Products
Figure 27: CLT Manufacturing Plant: Proposed Plant Layout