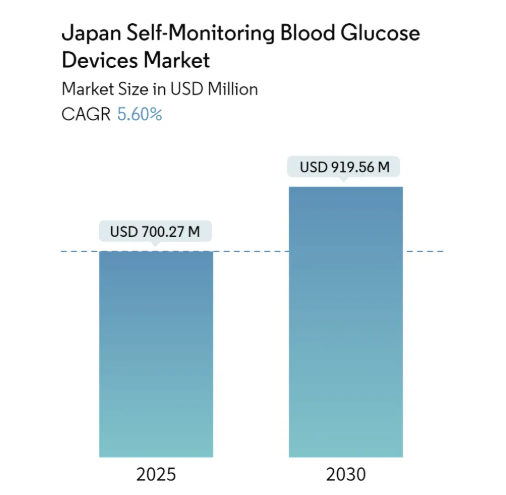
The Japan Self-Monitoring Blood Glucose (SMBG) Devices Market is projected to experience steady and significant growth over the forecast period, with an estimated market size of USD 700.27 million in 2025 and anticipated to reach USD 919.56 million by 2030, expanding at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 5.6%. This growth reflects Japan’s increasing focus on personalized healthcare management, particularly for chronic diseases such as diabetes, which continue to pose major public health challenges in the country. The adoption of SMBG devices enables patients to take an active role in managing their glucose levels, allowing them to make informed lifestyle, dietary, and treatment decisions. Regular self-monitoring helps individuals avoid glucose fluctuations that can lead to serious complications, including cardiovascular conditions, kidney failure, nerve damage, and vision problems. Accurate and timely monitoring supports early intervention, which is critical in preventing long-term complications and reducing the burden on the healthcare system.
Technology is playing a vital role in transforming blood glucose monitoring. The emergence of digital health tools and connected devices is significantly enhancing the utility of traditional SMBG devices. Advanced glucometers now offer integration with mobile applications, enabling users to track glucose readings over time, correlate results with meals, medication, and physical activity, and share data with healthcare professionals remotely. These features promote better disease self-management and foster greater patient adherence. Moreover, innovations such as insulin calculators, algorithm-driven insulin titration support, and virtual health coaching are further enhancing outcomes, especially for individuals with poorly controlled diabetes. These integrated solutions are becoming more prevalent in Japan’s evolving digital healthcare ecosystem.
On a global scale, the World Health Assembly has emphasized the importance of integrating diabetes care into primary healthcare systems. Recommendations include improving access to insulin, streamlining regulatory frameworks for diabetes-related products, and enhancing data collection and surveillance systems. Japan aligns with these global objectives through comprehensive national strategies that aim to improve diabetes care delivery and ensure continuity of treatment during emergencies or disasters. These initiatives contribute to a supportive regulatory environment that enhances the outlook of the SMBG devices market.
Rising prevalence of diabetes in Japan remains one of the most critical drivers of market growth. The country has an estimated 11 million people living with diabetes, with the number expected to rise in tandem with the aging population. Japan has one of the highest proportions of elderly citizens globally, a demographic that is particularly vulnerable to type 2 diabetes. As a result, the demand for self-monitoring devices is expected to increase steadily, supported by strong public awareness and early diagnosis programs. The ability to monitor glucose levels at home empowers patients to manage their condition proactively, reduce emergency visits, and avoid costly hospitalizations.
The Japanese healthcare system is well-developed, offering broad insurance coverage that includes diabetes monitoring tools and medications. Organizations such as the Japan Association for Diabetes Education and Care (JADEC) are actively involved in spreading awareness and supporting lifestyle modifications to prevent the onset of diabetes. Japan is considered a regional leader in preventive healthcare policy, with nationwide campaigns encouraging healthy living, balanced nutrition, and physical activity to minimize the incidence of adult-onset diabetes. These initiatives foster an environment where SMBG adoption is not only medically necessary but also socially encouraged.
One of the most important product segments within the Japan SMBG devices market is blood glucose test strips, which currently account for approximately 70% of the overall market share. Test strips are indispensable for daily glucose monitoring, offering fast and reliable results. When blood is placed on the strip, it reacts chemically and electrically to provide a glucose reading, which the glucometer then interprets. The high usage frequency of test strips, often multiple times per day, makes them a recurring cost component in diabetes care, unlike glucometers which are long-term investments. The recurring demand for test strips drives consistent revenue growth in this segment.
The dominance of test strips is attributed to their critical role in daily disease management and their single-use nature, which contrasts with the relatively infrequent need to replace glucometers. As such, the market for test strips is expected to grow at a faster pace than glucose meters. The Japanese Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare (MHLW) has recognized diabetes as a major health priority and continues to invest in disease prevention and patient support programs. Medical insurance in Japan covers most diabetes-related expenses, ensuring patient access to essential monitoring supplies like test strips and meters without financial burden.
With the rise in comorbidities such as hypertension and dyslipidemia among diabetes patients, overall treatment costs are rising. However, by improving access to monitoring tools and encouraging self-management practices, these costs can be managed more effectively. SMBG devices contribute to earlier detection of complications and better glycemic control, ultimately reducing healthcare expenditures. Innovations in test strip sensitivity and data integration capabilities further enhance their value in clinical practice.
In summary, Japan’s SMBG devices market is poised for robust growth, driven by a convergence of demographic, technological, regulatory, and economic factors. The rising burden of diabetes, coupled with public and private sector efforts to support early diagnosis and efficient disease management, continues to strengthen market demand. As technology advances and healthcare delivery becomes increasingly patient-centric, SMBG devices will play an even more integral role in Japan’s national health strategy. This evolving market offers considerable opportunities for stakeholders to introduce innovative, user-friendly, and data-integrated products that address the unique needs of Japanese consumers and healthcare providers alike.
Table of Contents
1. Introduction
-
1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
-
1.2 Scope of the Study
2. Research Methodology
3. Executive Summary
4. Market Dynamics
-
4.1 Market Overview
-
4.2 Market Drivers
-
4.3 Market Restraints
-
4.4 Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
-
4.4.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
-
4.4.2 Bargaining Power of Consumers
-
4.4.3 Threat of New Entrants
-
4.4.4 Threat of Substitute Products and Services
-
4.4.5 Intensity of Competitive Rivalry
-
5. Market Segmentation
-
5.1 By Component
-
5.1.1 Glucometer Devices
-
5.1.2 Test Strips
-
5.1.3 Lancets
-
6. Market Indicators
-
6.1 Type-1 Diabetes Population
-
6.2 Type-2 Diabetes Population
7. Competitive Landscape
-
7.1 Company Profiles
-
7.1.1 Abbott Diabetes Care
-
7.1.2 Roche Diabetes Care
-
7.1.3 LifeScan
-
7.1.4 Nipro
-
7.1.5 Arkray Inc.
-
7.1.6 Ascensia Diabetes Care
-
7.1.7 Menarini
-
7.1.8 Terumo
-
List Not Exhaustive
-
-
7.2 Company Share Analysis
-
7.2.1 Abbott Diabetes Care
-
7.2.2 Roche Diabetes Care
-
7.2.3 LifeScan
-
7.2.4 Other Company Share Analyses
-