1. Introduction
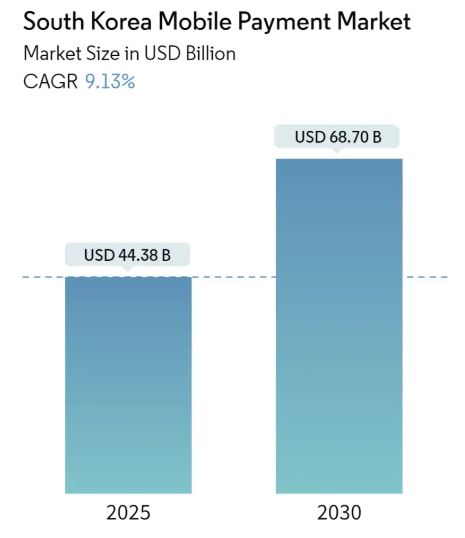
The South Korea mobile payment market is one of the most dynamic and rapidly evolving sectors in the country’s financial technology (fintech) landscape. Projected to grow from USD 44.38 billion in 2025 to USD 68.70 billion by 2030, with a CAGR of 9.13%, this market reflects the accelerated digital transformation taking place across the nation. The market is driven by several core factors including the surge in e-commerce, widespread smartphone penetration, consumer preference for contactless payments, and supportive government initiatives.
2. Market Overview
South Korea is one of the most digitally connected societies globally, with some of the highest smartphone and internet penetration rates. This digital maturity has set the stage for mobile payments to become a dominant method of transaction, overtaking traditional cash and card-based payments in many sectors. Leading domestic players such as Kakao Pay, Naver Pay, Samsung Pay, and Toss have created a competitive and innovative environment, offering user-friendly, secure, and seamless payment experiences.
3. Key Market Drivers
- Booming E-commerce Market: South Korea’s e-commerce market is thriving, accounting for nearly 8% of all retail sales and growing steadily. Mobile payment platforms are the preferred method for 65% of online purchases, as reported in 2022.
- Shift Towards Contactless and Proximity Payments: Post-pandemic behavioral changes have led to a surge in contactless transactions using QR codes and NFC-based systems.
- Integration of Mobile Payments into Daily Life: From taxis and cafes to public transportation and online platforms, mobile payments have become ubiquitous.
- Government Support: Initiatives such as Zero Pay promote mobile payments by offering tax benefits and subsidies to small and medium-sized businesses that adopt digital payment methods.
- Entry of Global Players: Companies like Apple Pay and PPRO have entered the market, bringing advanced technologies and encouraging competition.
4. Market Segmentation
By Payment Type
- Proximity Payments: Dominated by QR code and NFC-based payments, proximity payments are the largest segment due to convenience and widespread infrastructure.
- Remote Payments: Growing steadily with the expansion of online shopping and digital platforms.
By Application
- Retail and E-commerce: Significant contributor to mobile payment adoption, with consumers increasingly preferring mobile payments over cards.
- Public Transport: Integration with transport card systems has expanded usage.
- Food Delivery & Online-to-Offline (O2O) Services: Popular platforms like Baemin and Yogiyo have integrated mobile payment systems.
- Gaming and Digital Content: With South Korea’s leading position in the global gaming market, in-app purchases through mobile payments are highly popular.
5. Technological Trends
- 5G and Mobile Payment Synergy: Ultra-fast networks enable real-time payment processing and enhance security features.
- Biometric Authentication: Fingerprint, facial recognition, and iris scanning are being used for secure payments.
- Super Apps: Platforms like Kakao and Naver are combining messaging, e-commerce, payments, and financial services into all-in-one apps.
- Cross-border Payments: With rising tourism and international trade, seamless international mobile payment systems are gaining traction.
6. Competitive Landscape
Leading companies include:
- Kakao Pay: Backed by Kakao Corporation, with strong integration into Korea’s most popular messaging platform.
- Naver Pay: Integrated within Naver’s ecosystem, offering seamless e-commerce and digital payment services.
- Samsung Pay: Leveraging NFC and MST technologies for wide offline compatibility.
- Toss: A fintech unicorn focused on simple, fast, and user-friendly mobile payment and financial services.
- Apple Pay: Officially launched in South Korea in 2023, aiming to capture market share through its global ecosystem.
Recent strategic developments include the partnership between Samsung Pay and Naver Pay (March 2023) and BC Card’s partnership with Indonesian payment platforms (May 2022).
7. Challenges
- Cybersecurity Threats: The rise of digital payments also increases exposure to cyber-attacks and fraud.
- Market Saturation: The market is becoming highly competitive with limited differentiation between providers.
- Regulatory Compliance: Ongoing updates to financial and data protection laws may impose compliance costs.
8. COVID-19 Impact
The pandemic accelerated the shift to mobile payments as users and businesses sought safer, contactless methods. The preference for digital transactions is expected to persist post-pandemic, further driving market expansion.
9. Future Outlook (2025–2030)
The market is set to continue its robust growth trajectory, driven by:
- Expansion of e-commerce and O2O platforms.
- Growing demand for proximity payments.
- Government initiatives supporting digital transformation.
- Continuous innovation in security, speed, and convenience.
- Increasing foreign participation and technology inflows.
By 2030, South Korea’s mobile payment market is expected not only to expand domestically but also to position itself as a benchmark in the Asia-Pacific region for digital payment innovation and consumer adoption.
10. Strategic Recommendations
- Diversify Service Offerings: Companies should integrate value-added services such as micro-loans, insurance, and investment options.
- Strengthen Cybersecurity: Investing in security technology will be key to maintaining user trust.
- Expand International Partnerships: Collaboration with overseas platforms can enhance cross-border payment convenience.
- Focus on Elderly & Underserved Segments: Tailored payment solutions for older adults and low-tech users can drive inclusion.
The South Korean mobile payment market is poised for sustained growth, backed by technological leadership, strong consumer adoption, and an innovative business environment.
[Table of Contents]
1. Introduction
1.1 Study Assumptions and Market Definition
1.2 Scope of the Study
2. Research Methodology
3. Executive Summary
4. Market Insights
4.1 Market Overview
4.2 Market Size and Forecast of South Korea Mobile Payment Market
4.3 Industry Attractiveness – Porter’s Five Forces Analysis
4.3.1 Bargaining Power of Suppliers
4.3.2 Bargaining Power of Buyers/Consumers
4.3.3 Threat of New Entrants
4.3.4 Threat of Substitutes
4.3.5 Competitive Rivalry
4.4 Assessment of COVID-19 Impact on the Market
5. Market Dynamics
5.1 Market Drivers
5.1.1 Growing Adoption of Mobile Devices
5.1.2 Rising E-commerce and Online Shopping Trends
5.2 Market Restraints
5.2.1 Increasing Cybersecurity Threats
5.3 Key Regulations and Standards
5.4 Business Model Analysis
5.5 Market Penetration of Mobile Wallets
5.6 Enabling Technologies (NFC, QR, and Others)
5.7 Growth of Mobile Commerce and Its Impact on the Market
6. Market Segmentation
6.1 By Type
6.1.1 Proximity Payments
6.1.2 Remote Payments
7. Competitive Landscape
7.1 Company Profiles
7.1.1 Kakao Corporation (Kakao Pay)
7.1.2 Naver Corporation (Naver Pay)
7.1.3 Samsung Electronics (Samsung Pay)
7.1.4 Toss
7.1.5 PayCo
7.1.6 Smile Pay
7.1.7 Coupang (Rocket Pay)
7.1.8 SSG.com Corp. (SSG Pay)
7.1.9 SK Group (SK Pay)
7.1.10 L Pay
7.1.11 ZeroPay Pvt. Ltd. (Zero Pay)
(The list is not exhaustive)