1 はじめに 38
1.1 調査目的 38
1.2 市場の定義 38
1.2.1 包含と除外 39
1.3 市場範囲 39
1.3.1 市場セグメンテーション 40
1.3.2 考慮した年数 41
1.4 考慮した通貨 41
1.5 利害関係者 42
1.6 変化のまとめ 42
2 調査方法 44
2.1 調査データ 44
2.1.1 二次データ 45
2.1.2 一次データ 45
2.1.2.1 主要プロファイルの内訳 46
2.1.2.2 主要業界インサイト 46
2.2 市場ブレークアップとデータ三角測量 47
2.3 市場規模の推定 48
2.3.1 トップダウンアプローチ 48
2.3.2 ボトムアップアプローチ 49
2.4 市場予測 53
2.5 リサーチの前提 54
2.6 調査の限界 55
3 エグゼクティブサマリー 56
4 プレミアムインサイト 63
4.1 物流自動化市場におけるプレーヤーにとっての魅力的な機会 63
4.2 物流自動化市場:上位3社 64
4.3 北米の物流自動化市場:ロボットシステムと自動化ソフトウェア上位3社 64
4.4 物流自動化市場:地域別 65
5 市場概要と業界動向 66
5.1 はじめに 66
5.2 市場ダイナミクス
5.2.1 推進要因 67
5.2.1.1 電子商取引の増加 67
5.2.1.2 自律走行ロボットの採用増加 67
5.2.1.3 3PLサービスに対する需要の高まり 68
5.2.1.4 労働安全の必要性 68
5.2.2 阻害要因 68
5.2.2.1 統一されたガバナンス基準の欠如 68
5.2.2.2 高い設備投資 69
5.2.3 機会 69
5.2.3.1 自律走行車とドローンの導入 69
5.2.3.2 物流に革命をもたらすオートメーション・アズ・ア・サービス 69
5.2.3.3 インダストリー4.0の採用拡大 70
5.2.4 課題 70
5.2.4.1 既存システムとの統合 70
5.2.4.2 スタッフのトレーニングと労力に関する懸念 70
5.2.5 主要ユースケースと市場の可能性 71
5.2.5.1 主なユースケース 71
5.2.6 倉庫の自動化 72
5.2.7 経路最適化 72
5.2.8 予知保全 72
5.2.9 需要予測 73
5.2.10 自律走行車 73
5.2.11 サプライチェーンの可視化 73
5.3 物流自動化市場:進化 74
5.4 エコシステム分析 76
5.4.1 倉庫管理システム(WMS)プロバイダー 78
5.4.2 輸送管理システム(TMS)プロバイダー 79
5.4.3 自動認識・データ収集(AIDC)プロバイダー 79
5.4.4 自動保管・検索システム(As/Rs)プロバイダー 79
5.4.5 テクノロジーパートナー/インテグレーター 79
5.4.6 エンドユーザー 80
5.5 サプライチェーン分析 80
5.6 投資環境と資金調達シナリオ 81
5.7 ケーススタディ分析 82
5.7.1 ケーススタディ1:オーダーフルフィルメント強化に向けたヴェイヤーとデマティック社の提携 82
5.7.2 ケーススタディ 2: コカ・コーラボトラーズジャパンの埼玉メガDCにおける自動化と効率化 83
5.7.3 ケーススタディ3:ナップのエボシャトルシステムによるゲトリーバウ・ノルド社の変革 83
5.7.4 ケーススタディ4:ブルーヨンダーの在庫・受注管理ソリューションによるウォルグリーンの顧客体験の向上 84
5.7.5 ケーススタディ5:アシェットUKの革新的な配送センターの変革 85
5.8 テクノロジー分析 85
5.8.1 主要テクノロジー 86
5.8.1.1 ロボティック・プロセス・オートメーション(RPA) 86
5.8.1.2 人工知能(AI)と機械学習(ML) 86
5.8.1.3 ブロックチェーン 87
5.8.1.4 モノのインターネット(IoT) 87
5.8.1.5 拡張現実(AR)と仮想現実(VR) 88
5.8.2 補完技術 88
5.8.2.1 ビッグデータ分析 88
5.8.2.2 クラウドコンピューティング 89
5.8.2.3 デジタル・ツイン 89
5.8.3 隣接技術 90
5.8.3.1 サイバーセキュリティ 90
5.8.3.2 エッジコンピューティング 90
5.9 貿易分析 91
5.9.1 輸入シナリオ 91
5.9.2 輸出シナリオ 92
5.10 規制の状況 93
5.10.1 規制機関、政府機関、その他の組織 93
5.10.2 地域別規制 97
5.10.2.1 北米: 規制 97
5.10.2.1.1 奴隷解放事業認証法 97
5.10.2.1.2 米国の製造業を活性化し、重要なサプライチェーンを確保するためのバイデン-ハリス計画 98
5.10.2.1.3 連邦情報セキュリティ管理法(FISMA) 98
5.10.2.1.4 連邦情報処理標準(FIPS) 98
5.10.2.1.5 アメリカ COMPETES 法 99
5.10.2.2 欧州 規制 99
5.10.2.2.1 一般データ保護規則 99
5.10.2.2 欧州標準化委員会(CEN) 99
5.10.2.2.3 欧州電気通信標準化機構(ETSI) 100
5.10.2.2.4 企業の持続可能性デューディリジェンスに関する指令 100
5.10.2.2.5 指令 2014/24/EU: 公共調達 100
5.10.2.2.6 指令 2014/25/EU: 公益事業調達 101
5.10.2.3 アジア太平洋地域 101
5.10.2.3.1 ASEAN自由貿易協定(AFTA) 101
5.10.2.3.2 アジア太平洋貿易協定(APTA) 101
5.10.2.4 中東・アフリカ 102
5.10.2.4.1 連邦税関当局規制 102
5.10.2.5 ラテンアメリカ 102
5.10.2.5.1 道路、橋及び連邦交通に関する法律 102
5.10.2.5.2 1993年第105号法令 102
5.11 特許分析 103
5.11.1 方法論 103
5.11.2 出願特許(文書タイプ別) 103
5.11.3 技術革新と特許出願 103
5.12 価格分析 108
5.12.1 主要企業の平均販売価格動向(自動化システム) 108
5.12.2 指標価格分析(エンドユーザー別) 109
5.13 主要会議・イベント(2024-2025年) 110
5.14 ポーターの5つの力分析 111
5.14.1 新規参入の脅威 112
5.14.2 代替品の脅威 112
5.14.3 供給者の交渉力 112
5.14.4 買い手の交渉力 112
5.14.5 競合の激しさ 113
5.15 顧客ビジネスに影響を与えるトレンド/破壊 113
5.15.1 顧客ビジネスに影響を与えるトレンド/破壊 113
5.16 主要ステークホルダーと購買基準 114
5.16.1 購入プロセスにおける主要ステークホルダー 114
5.16.2 購入基準 115
5.17 地理的範囲別ロジスティクス 116
5.17.1 国内物流 116
5.17.2 国際物流 116
5.17.3 国境を越えた物流 117
6 物流自動化市場:提供サービス別 118
6.1 導入 119
6.1.1 オファリング 物流自動化市場の促進要因 119
6.2 自動化システム 121
6.2.1 メカニズムは精度と速度を高めるために高度なロボットとAIを活用 121
6.2.2 ロボットシステム 123
6.2.2.1 AGV(無人搬送車) 126
6.2.2.2 自律移動ロボット(AMR) 127
6.2.2.3 ロボットピッキングシステム 128
6.2.2.4 パレタイジング&デパレタイジングシステム 129
6.2.3 ストレージソリューション 130
6.2.3.1 自動保管・検索システム(AS/RS) 131
6.2.4 自動識別・データ収集(AIDC) 131
6.2.5 コンベア&ソーター 132
6.2.6 ドローン 133
6.3 自動化ソフトウェア 134
6.3.1 自動化システムにより在庫のリアルタイム追跡が容易になり、企業は在庫レベルを正確に保ち、再注文手順を自動化できる 134
6.3.2 輸送管理システム 136
6.3.2.1 リアルタイムの可視性と追跡 138
6.3.2.2 ルート最適化と輸送管理 138
6.3.2.3 フリート管理ソリューション 138
6.3.2.4 貨物監査・決済ソリューション 139
6.3.2.5 積荷最適化 139
6.3.3 倉庫管理システム(WMS) 140
6.3.3.1 在庫管理 141
6.3.3.1.1 在庫の最適化 141
6.3.3.1.2 在庫追跡 141
6.3.3.2 ヤード管理 142
6.3.3.3 出荷管理 142
6.3.3.4 労務管理 143
6.3.3.5 ベンダー管理 143
6.3.3.6 その他 143
6.3.4 受注管理ソフトウェア 144
6.3.4.1 チャットボットとデジタルアシスタント 145
6.3.4.2 文書・記録管理 145
6.3.4.3 販売会計処理 145
6.3.4.4 その他 146
6.4 導入形態別ソフトウェア 146
6.4.1 クラウド 148
6.4.2 オンプレミス 149
7 物流自動化市場:物流タイプ別 151
7.1 はじめに 152
7.1.1 物流タイプ別 物流自動化市場の促進要因 152
7.2 インバウンドロジスティクス 154
7.2.1 インバウンド・ロジスティクスは必要な時に必要な資源にアクセスできるようにし、効率的な生 産を維持する 154
7.2.2 調達物流 156
7.2.3 生産物流 157
7.3 アウトバウンド/販売物流 158
7.3.1 受注処理と配送効率の最適化における自動化によるアウトバウンド・ロジスティクスの強化 158
7.4 リバース・ロジスティクス 159
7.4.1 返品データを評価するためのAI搭載ツールにより、十分な情報に基づいた選択が可能に 159
8 ロジスティクス自動化市場:テクノロジー別 161
8.1 はじめに 162
8.1.1 テクノロジー:物流自動化市場の促進要因 162
8.2 ロボティクス・プロセス・オートメーション(RPA) 164
8.2.1 RPAはデータ入力、出荷追跡、文書管理を自動化することで業務効率と精度を向上 164
8.3 人工知能と分析 165
165 8.3.1 人工知能を搭載したシステムは、交通傾向、天候状況、配送タイムテーブルを調査することで、ルート編成を合理化することが可能 165
8.4 モノのインターネット(iot)プラットフォーム 166
8.4.1 出荷をリアルタイムで追跡することで、サプライヤーと流通業者はより効果的に連携でき、その結果、市場の変化に迅速に対応できる 166
8.5 ブロックチェーン 168
8.5.1 スマートコントラクトは支払いや通関など様々な業務を自動化 168
8.6 ビッグデータ 169
8.6.1 ビッグデータ分析の活用による物流業務の効率化と意思決定の強化 169
9 物流自動化市場:エンドユーザー別 170
9.1 はじめに 171
9.1.1 エンドユーザー:物流自動化市場の促進要因 171
9.2 企業タイプ別 172
9.2.1 小売・電子商取引 174
9.2.1.1 ロジスティクス自動化により、迅速で正確な注文処理と効率的な返品管理が可能に 174
9.2.2 医療・医薬品 175
9.2.2.1 ヘルスケア&医薬品業界におけるロジスティクス自動化は、業務効率の向上、規制遵守の徹底、製品の完全性の維持を実現 175
9.2.3 製造業 177
9.2.3.1 ロジスティクスの自動化は、製造業における高度なロボット工学とIoTの統合を通じて、ジャスト・イン・タイムの実践と持続可能性の目標をサポート 177
9.2.4 自動車 178
9.2.4.1 ロジスティクスの自動化は生産性を向上させ、自律型ロボットと高度なデジタルツールによるリアルタイムのデータ駆動型意思決定を可能にする 178
9.2.5 食品・飲料 179
9.2.5.1 高度な物流自動化技術による食品・飲料分野の効率性の向上とコンプライアンスの確保 179
9.2.6 金属・機械 180
9.2.6.1 先進的物流自動化技術による金属・機械分野の精密性と効率性 180
9.2.7 サードパーティ・ロジスティクス(3PL) 181
9.2.7.1 サードパーティー・ロジスティクスにおける業務効率化とサービス提供の強化 181
9.2.8 その他の企業タイプ 183
10 物流自動化市場:地域別 184
10.1 はじめに
10.2 北米 187
10.2.1 北米:物流自動化市場の促進要因 187
10.2.2 北米:マクロ経済見通し 187
10.2.3 米国 195
10.2.3.1 米国における物流市場の急成長と責任ある発展 195
10.2.4 カナダ 197
10.2.4.1 カナダの物流市場における戦略的成長: イノベーションとイニシアティブ 197
10.3 欧州 199
10.3.1 欧州: 物流自動化市場の促進要因
10.3.2 欧州:マクロ経済見通し マクロ経済見通し 199
10.3.3 イギリス 206
10.3.3.1 英国政府は自動化技術の発展を目指した研究開発の支援に積極的 206
10.3.4 フランス 208
10.3.4.1 フランスは低排出輸送ソリューションに注力 208
10.3.5 ドイツ 210
10.3.5.1 ドイツ政府は製造業と物流のデジタル化を通じてイノベーションを促進するインダストリー4.0を積極的に推進 210
10.3.6 イタリア 212
10.3.6.1 イタリアのデジタルの未来は政府関係者とビジネスパーソンの政策立案に役立つ 212
10.3.7 スペイン 214
10.3.7.1 スペイン政府はAIの変革の可能性を認識し、国家戦略を策定 214
10.3.8 その他の欧州 216
10.4 アジア太平洋地域 218
10.4.1 アジア太平洋地域:物流自動化市場の促進要因 219
10.4.2 アジア太平洋地域:マクロ経済見通し 219
10.4.3 中国 227
10.4.3.1 中国の物流ネットワークへのAI、ロボット工学、IoT技術の統合による高効率で拡張性の高いサプライチェーンの開発 227
10.4.4 インド 230
10.4.4.1 オンラインeコマース・プラットフォームの台頭により、サプライチェーンの合理化と運用コストの削減を目的とした自動倉庫システムの導入が増加 230
10.4.5 日本 232
10.4.5.1 eコマースの台頭と当日配送に対する消費者の期待の高さが自動化ソリューションの必要性を加速 232
10.4.6 韓国 234
10.4.6.1 通商産業省(MOTIE)は政府、ハイテク企業、学界のパートナーシップを通じてロジスティクスのイノベーションを推進 234
10.4.7 アンザス 236
10.4.7.1 広大な国土と農業、製造業、小売業などの成長により、オーストラリア・ニュージーランドでは効率的な物流業務が不可欠 236
10.4.8 その他のアジア太平洋地域 238
10.5 中東・アフリカ 241
10.5.1 中東・アフリカ:物流自動化市場の促進要因 241
10.5.2 中東・アフリカ:マクロ経済見通し 241
10.5.3 中東 249
10.5.3.1 サウジアラビア 250
10.5.3.1.1 リアルタイムの追跡とより良い在庫管理を可能にするスマート倉庫の台頭(サウジアラビア) 250
10.5.3.2 アラブ首長国連邦 252
10.5.3.2.1 意思決定能力を強化し、持続可能な慣行を促進するためのロジスティクス業務へのデータ分析と人工知能の導入 252
10.5.3.3 トルコ 254
10.5.3.3.1 トルコ政府は物流センターの開発や輸送網の強化など、インフラの近代化を目指したプロジェクトを開始 254
10.5.3.4 カタール 256
10.5.3.4.1 ブロックチェーン技術の統合が普及し、物流取引の透明性と安全性が向上 256
10.5.3.5 その他の中東地域 258
10.5.4 アフリカ 261
10.6 ラテンアメリカ 263
10.6.1 ラテンアメリカ:物流自動化市場の促進要因 263
10.6.2 ラテンアメリカ:マクロ経済見通し 264
10.6.3 ブラジル 271
10.6.3.1 複雑化する現代のサプライチェーン管理に不可欠な倉庫ロボットとインテリジェントシステムの採用増加 271
10.6.4 メキシコ 273
10.6.4.1 メキシコ政府はインフラ改善と外国直接投資の促進を目的としたイニシアティブを通じてデジタルトランスフォーメーションを推進 273
10.6.5 アルゼンチン 275
10.6.5.1 アルゼンチンでは電子商取引の台頭で自動化ソリューションへの需要が急増 275
10.6.6 その他のラテンアメリカ地域 277
11 競争環境 279
11.1 概要 279
11.2 主要企業の戦略/勝利への権利 279
11.3 収益分析 282
11.4 市場シェア分析 282
11.4.1 市場ランキング分析 283
11.5 製品比較分析 285
11.5.1 製品比較分析(倉庫管理システム別) 285
11.5.1.1 倉庫管理システム(ブルーヨンダー) 286
11.5.1.2 Manhattan SCALE(マンハッタン・アソシエイツ) 286
11.5.1.3 K.Motion Warehouse Advantage(Korber AG) 286
11.5.1.4 拡張倉庫管理(SAP) 286
11.5.1.5 倉庫管理クラウド(オラクル) 286
11.5.2 製品比較分析(輸送管理システム別) 287
11.5.2.1 Oracle Transportation Management(オラクル) 287
11.5.2.2 マンハッタンアクティブトランスポーテーションマネジメント(マンハッタン・アソシエイツ) 287
11.5.2.3 SAP 輸送管理(TM)(SAP) 288
11.5.2.4 ロジスティクスTMS(ロジスティクス) 288
11.5.2.5 ブルー・ヨンダー・ネットワーク・コントロール・タワー(Blue Yonder) 288
11.6 企業評価と財務指標 288
11.7 企業評価マトリックス:主要プレーヤー(2023年) 289
11.7.1 スター 289
11.7.2 新興リーダー 289
11.7.3 浸透型プレーヤー 290
11.7.4 参加企業 290
11.7.5 企業フットプリント:主要プレイヤー(2023年) 291
11.7.5.1 企業フットプリント 291
11.7.5.2 地域別フットプリント 292
11.7.5.3 オファリングのフットプリント 293
11.7.5.4 技術フットプリント 294
11.7.5.5 エンドユーザーフットプリント 295
11.8 企業評価マトリクス:新興企業/SM(2023年) 296
11.8.1 進歩的企業 296
11.8.2 対応力のある企業 296
11.8.3 ダイナミックな企業 296
11.8.4 スターティングブロック 296
11.8.5 競争ベンチマーキング:新興企業/SM(2023年) 298
11.8.5.1 主要新興企業/中小企業の詳細リスト 298
11.8.5.2 主要新興企業/SMEの競合ベンチマーキング 299
11.9 競争シナリオと動向 299
11.9.1 製品の発売と機能強化 299
11.9.2 取引 303
12 企業プロファイル 316
KION Group (Germany)
Honeywell (US)
Daifuku (Japan)
IBM (US)
SAP (Germany)
Oracle (US)
ABB (Switzerland)
Manhattan Associates (US)
KUKA Group (Germany)
Jungheinrich (Germany)
Toshiba (Japan)
Toyota Industries (Japan)
Zebra Technologies (US)
Kardex Group (Switzerland)
Symbotic (US)
KNAPP (Austria)
SSI Schaefer (Germany)
Blue Yonder (US)
Murata Machinery (Japan)
TGW Logistics (Austria)
Körber AG (Germany)
Beumer Group (Germany)
Mecalux International (Spain)
Hardis Group (France)
JR Automation (US)
Ecovium (Germany)
System Logistics (Italy)
Automated Logistics Systems (US)
Savoye (US)
Locus Robotics (US)
GreyOrange (US)
Falcon Autotech (India)
Logistically (US)
Logiwa (US) and Rossum (Czech Republic)
13 隣接市場と関連市場 394
13.1 はじめに 394
13.2 スマートウェアハウジング市場-2028年の世界予測 394
13.2.1 市場の定義 394
13.2.2 市場の概要 394
13.2.2.1 スマートウェアハウジング市場:オファリング別 396
13.2.2.2 スマートウェアハウジング市場:タイプ別ハードウェア 397
13.2.2.3 スマートウェアハウスの市場:タイプ別ソフトウェア 398
13.2.2.4 スマートウェアハウスのソフトウェア市場:デプロイメントモード別 399
13.2.2.5 スマートウェアハウスの市場:サービス別 400
13.2.2.6 スマートウェアハウスの市場:技術別 400
13.2.2.7 スマートウェアハウスの市場:アプリケーション別 401
13.2.2.8 スマートウェアハウジング市場:業種別 402
13.2.2.9 スマートウェアハウジング市場:地域別 403
13.3 サプライチェーン管理市場:2027年までの世界予測 404
13.3.1 市場の定義 404
13.3.2 市場の概要 404
13.3.2.1 サプライチェーン管理市場:コンポーネント別 406
13.3.2.2 サプライチェーン管理市場:ハードウェア別 407
13.3.2.3 サプライチェーン管理市場:タイプ別ソフトウェア 407
13.3.2.4 サプライチェーン管理市場:サービス別 408
13.3.2.5 サプライチェーン管理市場:展開形態別 409
13.3.2.6 サプライチェーン管理市場:組織規模別 410
13.3.2.7 サプライチェーン管理市場:業種別 410
13.3.2.8 サプライチェーン管理市場:地域別 411
14 付録 413
14.1 ディスカッションガイド 413
14.2 Knowledgestore: Marketsandmarketsの購読ポータル 419
14.3 カスタマイズオプション 421
14.4 関連レポート 421
14.5 著者の詳細 422
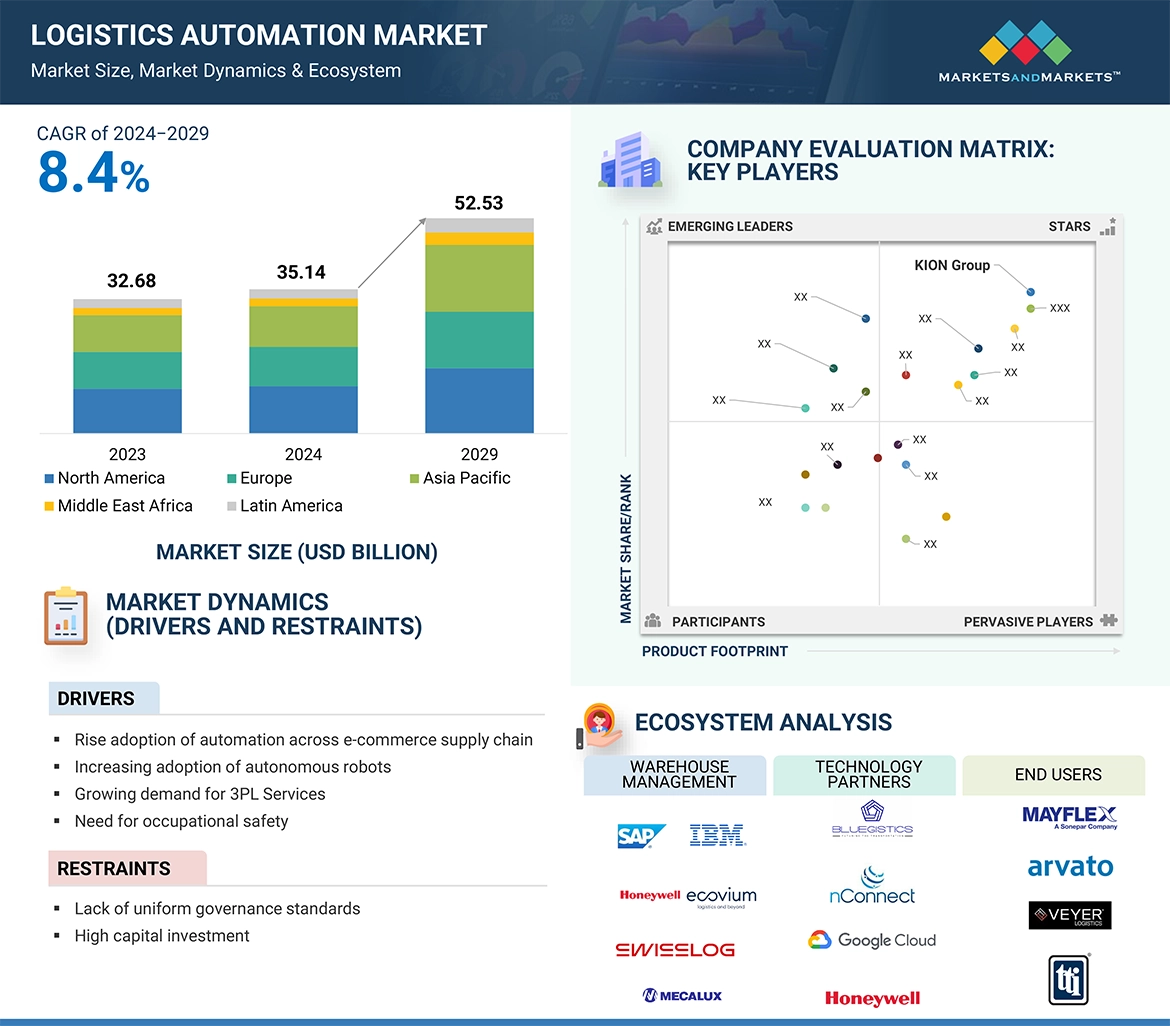
The market is anticipated to grow due to the rise of online retail and the demand for faster delivery, integration of AI, machine learning, and IoT in logistics systems, and growing labor shortages and rising labor costs have pushed companies to invest in automation technologies like robotics to maintain operational efficiency. However, growth may be restrained by the cost of implementing automation technologies, including robotics, AI, and autonomous vehicles, which can be prohibitively expensive, and the unexpected downtimes of automated logistics systems, which could disrupt logistics operations and lead to financial losses.
“Storage solutions segment is expected to hold the largest market share during the forecast period”
The storage solutions segment will hold the largest market share in logistics automation due to the growing demand for optimized warehouse space, driven by e-commerce and high-volume inventory management. Automated storage and retrieval systems (AS/RS) are key enablers, allowing companies to maximize storage density, reduce labor dependency, and enhance picking accuracy. AS/RS solutions also improve order processing speed and inventory tracking, crucial for meeting consumer expectations for faster delivery. Their ability to handle diverse inventory types and minimize warehouse footprints makes them indispensable for large-scale logistics operations.
“The retail and e-commerce enterprise type will have the fastest growth rate during the forecast period”
The retail and e-commerce sector within the enterprise segment is poised to have the fastest growth rate in the logistics automation market, driven by the rapid expansion of online shopping and the increasing demand for faster delivery services. Retailers and e-commerce platforms face immense pressure to optimize supply chains, reduce order processing times, and manage high-volume inventories. Automation technologies such as robotics, AI-driven warehouse management, and automated sorting systems are crucial in meeting these demands. Additionally, the surge in omnichannel retailing and same-day delivery expectations further fuels the need for automated logistics solutions in this sector.
“Asia Pacific's to witness rapid logistics automation growth fueled by innovation and emerging technologies”
The Asia Pacific region is expected to witness the fastest growth rate in the logistics automation market due to the rapid expansion of e-commerce, rising manufacturing activities, and increasing investments in infrastructure and technology by countries like China, India, and Japan. The region's large consumer base and the rise of online retail platforms have fueled the need for streamlined logistics processes, including automated warehouses, autonomous vehicles, and AI-powered inventory management systems. Additionally, government initiatives promoting smart manufacturing and digitalization, particularly in China and India, are accelerating the adoption of logistics automation technologies. Asia Pacific's robust infrastructure development, coupled with its focus on innovation and investment in automation technologies, positions it as the dominant player in the global logistics automation market.
Breakdown of primaries
In-depth interviews were conducted with Chief Executive Officers (CEOs), innovation and technology directors, system integrators, and executives from various key organizations operating in the Logistics Automation market.
By Company: Tier I – 34%, Tier II – 43%, and Tier III – 23%
By Designation: C-Level Executives – 50%, D-Level Executives – 30%, and others – 20%
By Region: North America – 30%, Europe – 25%, Asia Pacific – 35%, Middle East & Africa – 5%, and Latin America – 5%
The report includes the study of key players offering Logistics Automation solutions and services. It profiles major vendors in the Logistics Automation market. The major players in the Logistics Automation market include KION Group (Germany), Honeywell (US), Daifuku (Japan), IBM (US), SAP (Germany), Oracle (US), ABB (Switzerland), Manhattan Associates (US), KUKA Group (Germany), Jungheinrich (Germany), Toshiba (Japan), Toyota Industries (Japan), Zebra Technologies (US), Kardex Group (Switzerland), Symbotic (US), KNAPP (Austria), SSI Schaefer (Germany), Blue Yonder (US), Murata Machinery (Japan), TGW Logistics (Austria), Körber AG (Germany), Beumer Group (Germany), Mecalux International (Spain), Hardis Group (France), JR Automation (US), Ecovium (Germany), System Logistics (Italy), Automated Logistics Systems (US), Savoye (US), Locus Robotics (US), GreyOrange (US), Falcon Autotech (India), Logistically (US), Logiwa (US) and Rossum (Czech Republic).
Research coverage
This research report categorizes the Logistics Automation market By Offering (automated systems (robotic systems, storage solutions, automatic identification & data collection, others), automation software (transport management systems, warehouse management systems, order management software), software by deployment mode (cloud and on-premises)), By Logistics Type (inbound logistics (procurement logistics, production logistics), outbound/sales logistics, reverse logistics), By Technology (robotic process automation (RPA), artificial intelligence & analytics, internet of things (IoT) platform, blockchain, big data, others), By end user, enterprise type (retail & e-commerce, healthcare & pharmaceuticals, manufacturing, automotive, food & beverages, metal & machinery, third party-logistics (3PL), other enterprises), and By Region (North America, Europe, Asia Pacific, Middle East & Africa, and Latin America). The scope of the report covers detailed information regarding the major factors, such as drivers, restraints, challenges, and opportunities, influencing the growth of the logistics automation market. A detailed analysis of the key industry players has been done to provide insights into their business overview, products, and services; key strategies; contracts, partnerships, agreements, new product & service launches, mergers and acquisitions, and recent developments associated with the logistics automation market. Competitive analysis of upcoming startups in the logistics automation market ecosystem is covered in this report.
Key Benefits of Buying the Report
The report would provide the market leaders/new entrants in this market with information on the closest approximations of the revenue numbers for the overall logistics automation market and its subsegments. It would help stakeholders understand the competitive landscape and gain more insights better to position their business and plan suitable go-to-market strategies. It also helps stakeholders understand the pulse of the market and provides them with information on key market drivers, restraints, challenges, and opportunities.
The report provides insights on the following pointers:
•Analysis of key drivers (rise in e-commerce activities, increasing adoption of autonomous robots, growing demand for 3PL services, and need for occupational safety), restraints (lack of uniform governance standards and high capital investment), opportunities (implementation of autonomous vehicles & drones, automation-as-a-service to revolutionize logistics, and growing adoption of industry 4.0), and challenges (integration with existing systems and staff training and labor concerns).
•Product Development/Innovation: Detailed insights on upcoming technologies, research & development activities, and new product & service launches in the logistics automation market.
•Market Development: Comprehensive information about lucrative markets – the report analyses the logistics automation market across varied regions.
•Market Diversification: Exhaustive information about new products & services, untapped geographies, recent developments, and investments in the logistics automation market.
•Competitive Assessment: In-depth assessment of market shares, growth strategies and service offerings of leading players like KION Group (Germany), Honeywell (US), Daifuku (Japan), IBM (US), SAP (Germany), Oracle (US), ABB (Switzerland), Manhattan Associates (US), KUKA Group (Germany), Jungheinrich (Germany), Toshiba (Japan), Toyota Industries (Japan), Zebra Technologies (US), Kardex Group (Switzerland), Symbotic (US), KNAPP (Austria), SSI Schaefer (Germany), Blue Yonder (US), Murata Machinery (Japan), TGW Logistics (Austria), Körber AG (Germany), Beumer Group (Germany), Mecalux International (Spain), Hardis Group (France), JR Automation (US), Ecovium (Germany), System Logistics (Italy), Automated Logistics Systems (US), Savoye (US), Locus Robotics (US), GreyOrange (US), Falcon Autotech (India), Logistically (US), Logiwa (US) and Rossum (Czech Republic), among others in the logistics automation market. The report also helps stakeholders understand the pulse of the logistics automation market and provides them with information on key market drivers, restraints, challenges, and opportunities.
1 INTRODUCTION 38
1.1 STUDY OBJECTIVES 38
1.2 MARKET DEFINITION 38
1.2.1 INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS 39
1.3 MARKET SCOPE 39
1.3.1 MARKET SEGMENTATION 40
1.3.2 YEARS CONSIDERED 41
1.4 CURRENCY CONSIDERED 41
1.5 STAKEHOLDERS 42
1.6 SUMMARY OF CHANGES 42
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 44
2.1 RESEARCH DATA 44
2.1.1 SECONDARY DATA 45
2.1.2 PRIMARY DATA 45
2.1.2.1 Breakup of primary profiles 46
2.1.2.2 Key industry insights 46
2.2 MARKET BREAKUP AND DATA TRIANGULATION 47
2.3 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION 48
2.3.1 TOP-DOWN APPROACH 48
2.3.2 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH 49
2.4 MARKET FORECAST 53
2.5 RESEARCH ASSUMPTIONS 54
2.6 RESEARCH LIMITATIONS 55
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 56
4 PREMIUM INSIGHTS 63
4.1 ATTRACTIVE OPPORTUNITIES FOR PLAYERS IN LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET 63
4.2 LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET: TOP 3 ENTERPRISES 64
4.3 LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET IN NORTH AMERICA: TOP 3 ROBOTIC SYSTEMS AND AUTOMATION SOFTWARE 64
4.4 LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION 65
5 MARKET OVERVIEW AND INDUSTRY TRENDS 66
5.1 INTRODUCTION 66
5.2 MARKET DYNAMICS 66
5.2.1 DRIVERS 67
5.2.1.1 Rise in e-commerce activities 67
5.2.1.2 Increasing adoption of autonomous robots 67
5.2.1.3 Growing demand for 3PL services 68
5.2.1.4 Need for occupational safety 68
5.2.2 RESTRAINTS 68
5.2.2.1 Lack of uniform governance standards 68
5.2.2.2 High capital investment 69
5.2.3 OPPORTUNITIES 69
5.2.3.1 Implementation of autonomous vehicles and drones 69
5.2.3.2 Automation-as-a-service to revolutionize logistics 69
5.2.3.3 Growing adoption of Industry 4.0 70
5.2.4 CHALLENGES 70
5.2.4.1 Integration with existing systems 70
5.2.4.2 Staff training and labor concerns 70
5.2.5 TOP USE CASES & MARKET POTENTIAL 71
5.2.5.1 Key use cases 71
5.2.6 WAREHOUSE AUTOMATION 72
5.2.7 ROUTE OPTIMIZATION 72
5.2.8 PREDICTIVE MAINTENANCE 72
5.2.9 DEMAND FORECASTING 73
5.2.10 AUTONOMOUS VEHICLES 73
5.2.11 SUPPLY CHAIN VISIBILITY 73
5.3 LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET: EVOLUTION 74
5.4 ECOSYSTEM ANALYSIS 76
5.4.1 WAREHOUSE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (WMS) PROVIDERS 78
5.4.2 TRANSPORT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM (TMS) PROVIDERS 79
5.4.3 AUTOMATIC IDENTIFICATION & DATA CAPTURE (AIDC) PROVIDERS 79
5.4.4 AUTOMATED STORAGE & RETRIEVAL SYSTEM (AS/RS) 79
5.4.5 TECHNOLOGY PARTNERS/INTEGRATORS 79
5.4.6 END USERS 80
5.5 SUPPLY CHAIN ANALYSIS 80
5.6 INVESTMENT LANDSCAPE AND FUNDING SCENARIO 81
5.7 CASE STUDY ANALYSIS 82
5.7.1 CASE STUDY 1: VEYER'S PARTNERSHIP WITH DEMATIC FOR ENHANCED ORDER FULFILLMENT 82
5.7.2 CASE STUDY 2: AUTOMATION AND EFFICIENCY AT COCA-COLA BOTTLERS JAPAN'S SAITAMA MEGA DC 83
5.7.3 CASE STUDY 3: GETRIEBEBAU NORD'S TRANSFORMATION WITH KNAPP'S EVO SHUTTLE SYSTEM 83
5.7.4 CASE STUDY 4: WALGREENS ENHANCED CUSTOMER EXPERIENCE WITH BLUE YONDER'S INVENTORY AND ORDER MANAGEMENT SOLUTIONS 84
5.7.5 CASE STUDY 5: HACHETTE UK'S INNOVATIVE DISTRIBUTION CENTER TRANSFORMATION 85
5.8 TECHNOLOGY ANALYSIS 85
5.8.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES 86
5.8.1.1 Robotic Process Automation (RPA) 86
5.8.1.2 Artificial Intelligence (AI) & Machine Learning (ML) 86
5.8.1.3 Blockchain 87
5.8.1.4 Internet of Things (IoT) 87
5.8.1.5 Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) 88
5.8.2 COMPLEMENTARY TECHNOLOGIES 88
5.8.2.1 Big Data Analytics 88
5.8.2.2 Cloud Computing 89
5.8.2.3 Digital Twins 89
5.8.3 ADJACENT TECHNOLOGIES 90
5.8.3.1 Cybersecurity 90
5.8.3.2 Edge Computing 90
5.9 TRADE ANALYSIS 91
5.9.1 IMPORT SCENARIO 91
5.9.2 EXPORT SCENARIO 92
5.10 REGULATORY LANDSCAPE 93
5.10.1 REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS 93
5.10.2 REGULATIONS, BY REGION 97
5.10.2.1 North America: Regulations 97
5.10.2.1.1 Slave-Free Business Certification Act 97
5.10.2.1.2 Biden-Harris Plan to Revitalize American Manufacturing and Secure Critical Supply Chains 98
5.10.2.1.3 Federal Information Security Management Act (FISMA) 98
5.10.2.1.4 Federal Information Processing Standards (FIPS) 98
5.10.2.1.5 America COMPETES Act 99
5.10.2.2 Europe: Regulations 99
5.10.2.2.1 General Data Protection Regulation 99
5.10.2.2.2 European Committee for Standardization (CEN) 99
5.10.2.2.3 European Telecommunications Standards Institute (ETSI) 100
5.10.2.2.4 Directive on Corporate Sustainability Due Diligence 100
5.10.2.2.5 Directive 2014/24/EU: Public Procurement 100
5.10.2.2.6 Directive 2014/25/EU: Utilities Procurement 101
5.10.2.3 Asia Pacific 101
5.10.2.3.1 ASEAN Free Trade Agreement (AFTA) 101
5.10.2.3.2 Asia Pacific Trade Agreement (APTA) 101
5.10.2.4 Middle East & Africa 102
5.10.2.4.1 Federal Customs Authority Regulations 102
5.10.2.5 Latin America 102
5.10.2.5.1 Law on Roads, Bridges, and Federal Transport 102
5.10.2.5.2 Ley 105 de 1993 102
5.11 PATENT ANALYSIS 103
5.11.1 METHODOLOGY 103
5.11.2 PATENTS FILED, BY DOCUMENT TYPE 103
5.11.3 INNOVATION AND PATENT APPLICATIONS 103
5.12 PRICING ANALYSIS 108
5.12.1 AVERAGE SELLING PRICE TREND OF KEY PLAYERS, BY OFFERING (AUTOMATED SYSTEMS) 108
5.12.2 INDICATIVE PRICING ANALYSIS, BY END USER 109
5.13 KEY CONFERENCES AND EVENTS, 2024–2025 110
5.14 PORTER’S FIVE FORCES’ ANALYSIS 111
5.14.1 THREAT OF NEW ENTRANTS 112
5.14.2 THREAT OF SUBSTITUTES 112
5.14.3 BARGAINING POWER OF SUPPLIERS 112
5.14.4 BARGAINING POWER OF BUYERS 112
5.14.5 INTENSITY OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY 113
5.15 TRENDS/DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESS 113
5.15.1 TRENDS/DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESS 113
5.16 KEY STAKEHOLDERS & BUYING CRITERIA 114
5.16.1 KEY STAKEHOLDERS IN BUYING PROCESS 114
5.16.2 BUYING CRITERIA 115
5.17 LOGISTICS BY GEOGRAPHIC COVERAGE 116
5.17.1 DOMESTIC LOGISTICS 116
5.17.2 INTERNATIONAL LOGISTICS 116
5.17.3 CROSS-BORDER LOGISTICS 117
6 LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET, BY OFFERING 118
6.1 INTRODUCTION 119
6.1.1 OFFERING: LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET DRIVERS 119
6.2 AUTOMATED SYSTEMS 121
6.2.1 MECHANISMS UTILIZE SOPHISTICATED ROBOTS AND AI TO ENHANCE PRECISION AND VELOCITY 121
6.2.2 ROBOTICS SYSTEMS 123
6.2.2.1 Automated guided vehicles (AGVs) 126
6.2.2.2 Autonomous mobile robots (AMRs) 127
6.2.2.3 Robotic picking systems 128
6.2.2.4 Palletizing & depalletizing systems 129
6.2.3 STORAGE SOLUTIONS 130
6.2.3.1 Automated storage & retrieval systems (AS/RS) 131
6.2.4 AUTOMATED IDENTIFICATION AND DATA COLLECTION (AIDC) 131
6.2.5 CONVEYORS & SORTERS 132
6.2.6 DRONES 133
6.3 AUTOMATION SOFTWARE 134
6.3.1 AUTOMATED SYSTEMS MAKE IT EASIER TO TRACK INVENTORY IN REAL-TIME, ENABLING BUSINESSES TO KEEP STOCK LEVELS ACCURATE AND AUTOMATE REORDERING PROCEDURES 134
6.3.2 TRANSPORT MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS 136
6.3.2.1 Real-time visibility and tracking 138
6.3.2.2 Route optimization and transportation management 138
6.3.2.3 Fleet management solutions 138
6.3.2.4 Freight audit and payment solutions 139
6.3.2.5 Load optimization 139
6.3.3 WAREHOUSE MANAGEMENT SYSTEMS (WMS) 140
6.3.3.1 Inventory management 141
6.3.3.1.1 Inventory optimization 141
6.3.3.1.2 Inventory tracking 141
6.3.3.2 Yard management 142
6.3.3.3 Shipping management 142
6.3.3.4 Labor management 143
6.3.3.5 Vendor management 143
6.3.3.6 Others 143
6.3.4 ORDER MANAGEMENT SOFTWARE 144
6.3.4.1 Chatbot and digital assistants 145
6.3.4.2 Document and records management 145
6.3.4.3 Sales accounting processing 145
6.3.4.4 Others 146
6.4 SOFTWARE BY DEPLOYMENT MODE 146
6.4.1 CLOUD 148
6.4.2 ON-PREMISES 149
7 LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET, BY LOGISTICS TYPE 151
7.1 INTRODUCTION 152
7.1.1 LOGISTICS TYPE: LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET DRIVERS 152
7.2 INBOUND LOGISTICS 154
7.2.1 INBOUND LOGISTICS MAKE SURE THAT ESSENTIAL RESOURCES ARE ACCESSIBLE WHENEVER REQUIRED, MAINTAINING EFFICIENT PRODUCTION 154
7.2.2 PROCUREMENT LOGISTICS 156
7.2.3 PRODUCTION LOGISTICS 157
7.3 OUTBOUND/SALES LOGISTICS 158
7.3.1 ENHANCING OUTBOUND LOGISTICS THROUGH AUTOMATION IN OPTIMIZING ORDER FULFILLMENT AND DELIVERY EFFICIENCY 158
7.4 REVERSE LOGISTICS 159
7.4.1 AI-POWERED TOOLS TO EVALUATE DATA FROM RETURNS MADE, ENABLING THEM TO MAKE INFORMED CHOICES 159
8 LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET, BY TECHNOLOGY 161
8.1 INTRODUCTION 162
8.1.1 TECHNOLOGY: LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET DRIVERS 162
8.2 ROBOTICS PROCESS AUTOMATION (RPA) 164
8.2.1 RPA BOOSTS OPERATIONAL EFFICIENCY AND ACCURACY BY AUTOMATING DATA ENTRY, SHIPMENT TRACKING, AND DOCUMENT MANAGEMENT 164
8.3 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE & ANALYTICS 165
8.3.1 AI-POWERED SYSTEMS CAN STREAMLINE ROUTE ORGANIZATION BY EXAMINING TRAFFIC TRENDS, WEATHER CIRCUMSTANCES, AND DELIVERY TIMETABLES 165
8.4 INTERNET OF THINGS (IOT) PLATFORM 166
8.4.1 TRACKING SHIPMENTS IN REAL-TIME, SUPPLIERS AND DISTRIBUTORS CAN COORDINATE MORE EFFECTIVELY, RESULTING IN QUICKER REACTION TO CHANGES IN MARKET 166
8.5 BLOCKCHAIN 168
8.5.1 SMART CONTRACTS AUTOMATE DIFFERENT TASKS, LIKE PAYMENTS AND CUSTOMS CLEARANCE 168
8.6 BIG DATA 169
8.6.1 LEVERAGING BIG DATA ANALYTICS FOR ENHANCED EFFICIENCY AND DECISION-MAKING IN LOGISTICS OPERATIONS 169
9 LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET, BY END USER 170
9.1 INTRODUCTION 171
9.1.1 END USER: LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET DRIVERS 171
9.2 BY ENTERPRISE TYPE 172
9.2.1 RETAIL & E-COMMERCE 174
9.2.1.1 Logistics automation enables rapid, accurate order fulfillment and efficient returns management 174
9.2.2 HEALTHCARE & PHARMACEUTICALS 175
9.2.2.1 Logistics automation in healthcare & pharmaceuticals enhances operational efficiency, ensures regulatory compliance, and maintains product integrity 175
9.2.3 MANUFACTURING 177
9.2.3.1 Logistics automation supports just-in-time practices and sustainability goals through advanced robotics and IoT integration in manufacturing 177
9.2.4 AUTOMOTIVE 178
9.2.4.1 Logistics automation enhances productivity and enables real-time data-driven decision-making through autonomous robots and advanced digital tools 178
9.2.5 FOOD & BEVERAGE 179
9.2.5.1 Enhancing efficiency and ensuring compliance in food & beverage sector through advanced logistics automation technologies 179
9.2.6 METAL & MACHINERY 180
9.2.6.1 Precision and efficiency in metal & machinery sector through advanced logistics automation technologies 180
9.2.7 THIRD-PARTY LOGISTICS (3PL) 181
9.2.7.1 Enhancing operational efficiency and service delivery in third-party logistics 181
9.2.8 OTHER ENTERPRISE TYPES 183
10 LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET, BY REGION 184
10.1 INTRODUCTION 185
10.2 NORTH AMERICA 187
10.2.1 NORTH AMERICA: LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET DRIVERS 187
10.2.2 NORTH AMERICA: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK 187
10.2.3 US 195
10.2.3.1 Rapid growth and responsible development of logistics market in US 195
10.2.4 CANADA 197
10.2.4.1 Canada's strategic growth in logistics market: Innovations and initiatives 197
10.3 EUROPE 199
10.3.1 EUROPE: LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET DRIVERS 199
10.3.2 EUROPE: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK 199
10.3.3 UK 206
10.3.3.1 UK government has been proactive in supporting research and development efforts aimed at advancing automation technologies 206
10.3.4 FRANCE 208
10.3.4.1 France focuses on low-emission transport solutions 208
10.3.5 GERMANY 210
10.3.5.1 German government has been actively promoting Industry 4.0 to foster innovation through digitalization in manufacturing and logistics 210
10.3.6 ITALY 212
10.3.6.1 Digital future for Italy will help government officials and businesspersons shape their policies 212
10.3.7 SPAIN 214
10.3.7.1 Spanish government has recognized transformative potential of AI and developed national strategy 214
10.3.8 REST OF EUROPE 216
10.4 ASIA PACIFIC 218
10.4.1 ASIA PACIFIC: LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET DRIVERS 219
10.4.2 ASIA PACIFIC: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK 219
10.4.3 CHINA 227
10.4.3.1 Integration of AI, robotics, and IoT technologies into China’s logistics networks leading to development of highly efficient and scalable supply chains 227
10.4.4 INDIA 230
10.4.4.1 Rise of online e-commerce platforms leading to adoption of automated warehousing systems to streamline supply chains and reduce operational costs 230
10.4.5 JAPAN 232
10.4.5.1 Rise of e-commerce, coupled with high consumer expectations for same-day delivery, has accelerated need for automated solutions 232
10.4.6 SOUTH KOREA 234
10.4.6.1 Ministry of Trade, Industry, and Energy (MOTIE) to push for innovation in logistics through partnerships between government, tech companies, and academia 234
10.4.7 ANZ 236
10.4.7.1 Vast geographical expanse and growth of sectors such as agriculture, manufacturing, and retail make efficient logistics operations essential in Australia & New Zealand 236
10.4.8 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC 238
10.5 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA 241
10.5.1 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA: LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET DRIVERS 241
10.5.2 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK 241
10.5.3 MIDDLE EAST 249
10.5.3.1 Saudi Arabia 250
10.5.3.1.1 Rise of smart warehouses to enable real-time tracking and better inventory management in Saudi Arabia 250
10.5.3.2 UAE 252
10.5.3.2.1 Incorporation of data analytics and artificial intelligence in logistics operations to enhance decision-making capabilities and promote sustainable practices 252
10.5.3.3 Turkey 254
10.5.3.3.1 Turkey's government launches projects aimed at modernizing infrastructure, including development of logistics centers and enhancement of transportation networks 254
10.5.3.4 QATAR 256
10.5.3.4.1 Integration of blockchain technology to gain traction, enhancing transparency and security in logistics transactions 256
10.5.3.5 Rest of Middle East 258
10.5.4 AFRICA 261
10.6 LATIN AMERICA 263
10.6.1 LATIN AMERICA: LOGISTICS AUTOMATION MARKET DRIVERS 263
10.6.2 LATIN AMERICA: MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK 264
10.6.3 BRAZIL 271
10.6.3.1 Increasing adoption of warehouse robotics and intelligent systems, which are essential for managing complexities of modern supply chains 271
10.6.4 MEXICO 273
10.6.4.1 Mexican government promotes digital transformation through initiatives aimed at improving infrastructure and facilitating foreign direct investment 273
10.6.5 ARGENTINA 275
10.6.5.1 Rise of e-commerce in Argentina has created pressing demand for automated solutions 275
10.6.6 REST OF LATIN AMERICA 277
11 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE 279
11.1 OVERVIEW 279
11.2 KEY PLAYER STRATEGIES/RIGHT TO WIN 279
11.3 REVENUE ANALYSIS 282
11.4 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS 282
11.4.1 MARKET RANKING ANALYSIS 283
11.5 PRODUCT COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS 285
11.5.1 PRODUCT COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS, BY WAREHOUSE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM 285
11.5.1.1 Warehouse Management System (Blue Yonder) 286
11.5.1.2 Manhattan SCALE (Manhattan Associates) 286
11.5.1.3 K.Motion Warehouse Advantage (Korber AG) 286
11.5.1.4 Extended Warehouse Management (SAP) 286
11.5.1.5 Warehouse Management Cloud (Oracle) 286
11.5.2 PRODUCT COMPARATIVE ANALYSIS, BY TRANSPORT MANAGEMENT SYSTEM 287
11.5.2.1 Oracle Transportation Management (Oracle) 287
11.5.2.2 Manhattan Active Transportation Management (Manhattan Associates) 287
11.5.2.3 SAP Transportation Management (TM) (SAP) 288
11.5.2.4 Logistically TMS (Logistically) 288
11.5.2.5 Blue Yonder Network Control Tower (Blue Yonder) 288
11.6 COMPANY VALUATION AND FINANCIAL METRICS 288
11.7 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: KEY PLAYERS, 2023 289
11.7.1 STARS 289
11.7.2 EMERGING LEADERS 289
11.7.3 PERVASIVE PLAYERS 290
11.7.4 PARTICIPANTS 290
11.7.5 COMPANY FOOTPRINT: KEY PLAYERS, 2023 291
11.7.5.1 Company Footprint 291
11.7.5.2 Region Footprint 292
11.7.5.3 Offering Footprint 293
11.7.5.4 Technology Footprint 294
11.7.5.5 End User Footprint 295
11.8 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: STARTUPS/SMES, 2023 296
11.8.1 PROGRESSIVE COMPANIES 296
11.8.2 RESPONSIVE COMPANIES 296
11.8.3 DYNAMIC COMPANIES 296
11.8.4 STARTING BLOCKS 296
11.8.5 COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING: STARTUPS/SMES, 2023 298
11.8.5.1 Detailed List of Key Startups/SMEs 298
11.8.5.2 Competitive Benchmarking of Key Startups/SMEs 299
11.9 COMPETITIVE SCENARIO AND TRENDS 299
11.9.1 PRODUCT LAUNCHES AND ENHANCEMENTS 299
11.9.2 DEALS 303
12 COMPANY PROFILES 316
12.1 INTRODUCTION 316
12.1.1 KION GROUP 316
12.1.1.1 Business overview 316
12.1.1.2 Products offered 318
12.1.1.3 Recent developments 319
12.1.1.3.1 Product Launches and Enhancements 319
12.1.1.3.2 Deals 319
12.1.1.3.3 Expansions 320
12.1.1.4 MnM view 321
12.1.1.4.1 Right to win 321
12.1.1.4.2 Strategic choices 321
12.1.1.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats 321
12.1.2 HONEYWELL 322
12.1.2.1 Business overview 322
12.1.2.2 Products offered 323
12.1.2.3 Recent developments 324
12.1.2.3.1 Product Launches and Enhancements 324
12.1.2.3.2 Deals 325
12.1.2.4 MnM view 326
12.1.2.4.1 Right to win 326
12.1.2.4.2 Strategic choices 326
12.1.2.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats 326
12.1.3 DAIFUKU 327
12.1.3.1 Business overview 327
12.1.3.2 Products offered 328
12.1.3.3 Recent developments 329
12.1.3.3.1 Product Launches 329
12.1.3.3.2 Deals 330
12.1.3.4 MnM view 331
12.1.3.4.1 Right to win 331
12.1.3.4.2 Strategic choices 331
12.1.3.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats 331
12.1.4 IBM 332
12.1.4.1 Business overview 332
12.1.4.2 Products offered 333
12.1.4.3 Recent developments 334
12.1.4.3.1 Product Enhancements 334
12.1.4.3.2 Deals 335
12.1.4.4 MnM view 336
12.1.4.4.1 Right to win 336
12.1.4.4.2 Strategic choices 336
12.1.4.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats 337
12.1.5 SAP 338
12.1.5.1 Business overview 338
12.1.5.2 Products offered 339
12.1.5.3 Recent developments 340
12.1.5.3.1 Product Enhancements 340
12.1.5.3.2 Deals 341
12.1.5.4 MnM view 342
12.1.5.4.1 Right to win 342
12.1.5.4.2 Strategic choices 342
12.1.5.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats 343
12.1.6 SAMSUNG SDS 344
12.1.6.1 Business overview 344
12.1.6.2 Products offered 345
12.1.6.3 Recent developments 346
12.1.6.3.1 Product Launches 346
12.1.6.3.2 Deals 347
12.1.7 ORACLE 348
12.1.7.1 Business overview 348
12.1.7.2 Products offered 349
12.1.7.3 Recent developments 351
12.1.7.3.1 Product Enhancements 351
12.1.7.3.2 Deals 352
12.1.8 ABB 353
12.1.8.1 Business overview 353
12.1.8.2 Products offered 354
12.1.8.3 Recent developments 355
12.1.8.3.1 Product Enhancements 355
12.1.8.3.2 Deals 356
12.1.9 MANHATTAN ASSOCIATES 357
12.1.9.1 Business overview 357
12.1.9.2 Products offered 358
12.1.9.3 Recent developments 359
12.1.9.3.1 Deals 359
12.1.10 KUKA AG 361
12.1.10.1 Business overview 361
12.1.10.2 Products offered 362
12.1.10.3 Recent developments 363
12.1.10.3.1 Deals 363
12.1.11 JUNGHEINRICH 365
12.1.11.1 Business overview 365
12.1.11.2 Products offered 366
12.1.11.3 Recent developments 367
12.1.11.3.1 Product Launches 367
12.1.11.3.2 Deals 368
12.1.12 TOSHIBA 369
12.1.13 TOYOTA INDUSTRIES 370
12.1.14 ZEBRA TECHNOLOGIES 371
12.1.15 KARDEX GROUP 372
12.1.16 SYMBOTIC 373
12.1.17 KNAPP 374
12.1.18 SSI SCHAEFER 375
12.1.19 BLUE YONDER 376
12.1.20 MURATA MACHINERY 377
12.1.21 TGW LOGISTICS GROUP 378
12.1.22 KÖRBER AG 379
12.1.23 BEUMER GROUP 380
12.1.24 MECALUX INTERNATIONAL 381
12.1.25 HARDIS GROUP 382
12.1.26 JR AUTOMATION 382
12.2 STARTUP/SME PROFILES 383
12.2.1 ECOVIUM 383
12.2.2 SYSTEM LOGISTICS 384
12.2.3 AUTOMATED LOGISTICS SYSTEMS 385
12.2.4 SAVOYE 386
12.2.5 LOCUS ROBOTICS 387
12.2.6 GREYORANGE 388
12.2.7 FALCON AUTOTECH 389
12.2.8 LOGISTICALLY 390
12.2.9 LOGIWA 390
12.2.10 ROSSUM 391
12.2.11 RIGHTHAND ROBOTICS 391
12.2.12 THIRD WAVE AUTOMATION 392
12.2.13 AGILITY ROBOTICS 392
12.2.14 GATHER AI 393
13 ADJACENT AND RELATED MARKETS 394
13.1 INTRODUCTION 394
13.2 SMART WAREHOUSING MARKET—GLOBAL FORECAST 2028 394
13.2.1 MARKET DEFINITION 394
13.2.2 MARKET OVERVIEW 394
13.2.2.1 Smart Warehousing Market, by Offering 396
13.2.2.2 Smart Warehousing Market, Hardware by Type 397
13.2.2.3 Smart Warehousing Market, Software by Type 398
13.2.2.4 Smart Warehousing Software Market, by Deployment Mode 399
13.2.2.5 Smart Warehousing Market, by Service 400
13.2.2.6 Smart Warehousing Market, by Technology 400
13.2.2.7 Smart Warehousing Market, by Application 401
13.2.2.8 Smart Warehousing Market, by Vertical 402
13.2.2.9 Smart Warehousing Market, by Region 403
13.3 SUPPLY CHAIN MANAGEMENT MARKET — GLOBAL FORECAST TO 2027 404
13.3.1 MARKET DEFINITION 404
13.3.2 MARKET OVERVIEW 404
13.3.2.1 Supply Chain Management Market, by Component 406
13.3.2.2 Supply Chain Management Market, by Hardware 407
13.3.2.3 Supply Chain Management Market, Software by Type 407
13.3.2.4 Supply Chain Management Market, by Service 408
13.3.2.5 Supply Chain Management Market, by Deployment Mode 409
13.3.2.6 Supply Chain Management Market, by Organization Size 410
13.3.2.7 Supply Chain Management Market, by Vertical 410
13.3.2.8 Supply Chain Management Market, by Region 411
14 APPENDIX 413
14.1 DISCUSSION GUIDE 413
14.2 KNOWLEDGESTORE: MARKETSANDMARKETS’ SUBSCRIPTION PORTAL 419
14.3 CUSTOMIZATION OPTIONS 421
14.4 RELATED REPORTS 421
14.5 AUTHOR DETAILS 422
❖ 世界の物流自動化市場に関するよくある質問(FAQ) ❖
・物流自動化の世界市場規模は?
→MarketsandMarkets社は2024年の物流自動化の世界市場規模を351億4,000万米ドルと推定しています。
・物流自動化の世界市場予測は?
→MarketsandMarkets社は2029年の物流自動化の世界市場規模を525億3,000万米ドルと予測しています。
・物流自動化市場の成長率は?
→MarketsandMarkets社は物流自動化の世界市場が2024年~2029年に年平均8.4%成長すると予測しています。
・世界の物流自動化市場における主要企業は?
→MarketsandMarkets社は「KION Group (Germany)、Honeywell (US)、Daifuku (Japan)、IBM (US)、SAP (Germany)、Oracle (US)、ABB (Switzerland)、Manhattan Associates (US)、KUKA Group (Germany)、Jungheinrich (Germany)、Toshiba (Japan)、Toyota Industries (Japan)、Zebra Technologies (US)、Kardex Group (Switzerland)、Symbotic (US)、KNAPP (Austria)、SSI Schaefer (Germany)、Blue Yonder (US)、Murata Machinery (Japan)、TGW Logistics (Austria)、Körber AG (Germany)、Beumer Group (Germany)、Mecalux International (Spain)、Hardis Group (France)、JR Automation (US)、Ecovium (Germany)、System Logistics (Italy)、Automated Logistics Systems (US)、Savoye (US)、Locus Robotics (US)、GreyOrange (US)、Falcon Autotech (India)、Logistically (US)、Logiwa (US) and Rossum (Czech Republic)など ...」をグローバル物流自動化市場の主要企業として認識しています。
※上記FAQの市場規模、市場予測、成長率、主要企業に関する情報は本レポートの概要を作成した時点での情報であり、納品レポートの情報と少し異なる場合があります。