1 はじめに 27
1.1 調査目的 27
1.2 市場の定義 27
1.3 調査範囲 28
1.3.1 対象範囲と除外項目 28
1.3.2 対象市場と地域範囲 29
1.3.3 考慮した年数 30
1.4 考慮した通貨 30
1.5 単位の検討 30
1.6 調査の限界 30
1.7 利害関係者 31
1.8 変更点のまとめ 31
2 調査方法 32
2.1 調査データ 32
2.2 一次調査および二次調査 33
2.2.1 二次データ 33
2.2.2 二次ソースからの主要データ 33
2.2.3 一次データ 34
2.2.3.1 一次ソースからの主要データ 34
2.2.3.2 一次データの内訳 35
2.3 市場規模の推定 36
2.3.1 ボトムアップアプローチ 36
2.3.2 トップダウンアプローチ 37
2.3.3 需要サイド分析 38
2.3.3.1 需要サイド分析の前提条件 38
2.3.3.2 需要側分析の計算 39
2.3.4 供給側分析 39
2.3.4.1 供給側分析の計算 40
2.3.4.2 供給側分析の前提条件 40
2.4 市場の内訳とデータの三角測量 41
2.5 予測 41
2.6 リスク評価 42
3 エグゼクティブ・サマリー 43
4 プレミアムインサイト 49
4.1 小型モジュール炉市場におけるプレイヤーの魅力的な機会 49
4.2 小型モジュール炉市場:地域別 50
4.3 小型モジュール炉市場:冷却材別 50
4.4 小型モジュール炉市場:タイプ別 51
4.5 小型モジュール炉市場:接続性別 51
4.6 小型モジュール炉市場:配置別 51
4.7 小型モジュール炉市場:場所別 52
4.8 小型モジュール炉市場:用途別 52
4.9 小型モジュール炉市場:定格出力別 52
4.10 アジア太平洋地域の小型モジュール炉市場:タイプ別、国別 53
5 市場の概要
5.1 導入 54
5.2 市場ダイナミクス
5.2.1 推進要因
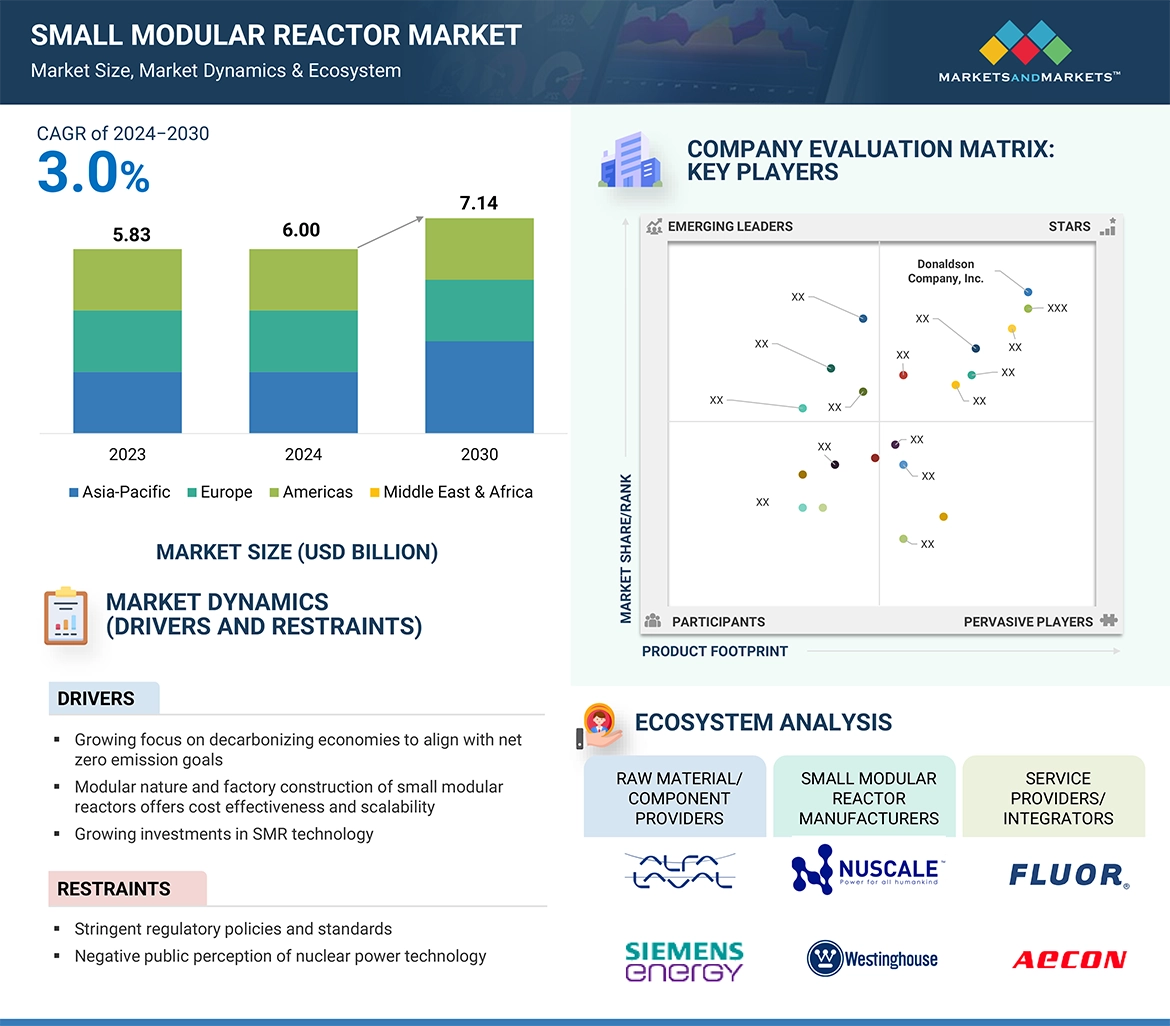
5.2.1.1 ネット・ゼロ・エミッション目標に向けた脱炭素化への関心の高まり 55
5.2.1.2 モジュール式と工場建設による費用対効果と拡張性 56
5.2.1.3 SMR 技術への投資の増加 56
5.2.2 阻害要因 56
5.2.2.1 厳しい規制政策と基準 56
5.2.2.2 原子力技術に対する否定的な社会認識 57
5.2.3 機会 57
5.2.3.1 原子力事業に伴うリスクの最小化 57
5.2.3.2 SMR と再生可能エネルギー源の統合 58
5.2.4 課題 59
5.2.4.1 標準的な許認可プロセスの欠如 59
5.3 顧客ビジネスに影響を与える傾向/混乱 59
5.4 サプライチェーン分析 60
5.5 エコシステム分析 61
5.6 データセンター/AI 企業からの Smr/原子力エネルギーへの投資 62
5.7 技術分析 62
5.7.1 主要技術 62
5.7.1.1 核分裂 62
5.7.1.2 軽水炉 62
5.7.1.3 重水炉 62
5.7.1.4 高速中性子炉 63
5.7.1.5 溶融塩炉 63
5.7.2 補完技術 63
5.7.2.1 再生可能エネルギーの統合 63
5.7.2.2 スマートグリッドの統合 63
5.7.3 隣接技術 64
5.7.3.1 水素製造 64
5.8 ケーススタディ分析 64
5.8.1 フィンランド政府、炭素排出削減のための代替システムに関する法律を制定 64
5.8.2 Nuscale Power, LLC がクリーンエネルギー目標達成のためアイダホ国立研 究所で Voygr 展開の設計承認を取得 64
5.8.3 足場ソリューションがサウスカロライナ州の原子力発電所の監視、検査、保守を支援 65
5.9 特許分析 66
5.10 価格分析 68
5.10.1 平均価格動向(タイプ別) 68
5.10.2 価格動向(地域別) 69
5.11 貿易分析 69
5.11.1 輸入シナリオ 69
5.11.2 輸出シナリオ 70
5.12 主要会議・イベント(2024~2025年) 71
5.13 規制情勢 72
5.13.1 規制機関、政府機関、その他の組織 72
5.13.2 規制の枠組み/政策 75
5.13.2.1 米州における規制の枠組み/政策 75
5.13.2.2 アジア太平洋地域の規制の枠組み/政策 76
5.13.2.3 欧州における規制の枠組み/政策 76
5.14 ポーターの5つの力分析 77
5.14.1 代替品の脅威 78
5.14.2 供給者の交渉力 78
5.14.3 買い手の交渉力 78
5.14.4 新規参入の脅威 79
5.14.5 競合の激しさ 79
5.15 主要ステークホルダーと購買基準 79
5.15.1 購入プロセスにおける主要ステークホルダー 79
5.15.2 購入基準 80
5.16 投資と資金調達のシナリオ 81
5.17 小型モジュール炉市場における生成aiの影響 81
5.17.1 小型モジュール炉市場におけるジェネレーティブAIの採用 81
5.17.2 ジェネレーティブAIの影響(アプリケーション別) 82
5.17.3 小型モジュール炉市場におけるジェネレーティブAIの影響(地域別) 82
5.18 小型モジュール炉市場のマクロ経済展望 83
6 小型モジュール炉市場:定格出力別 85
6.1 導入 86
6.2 100MWまで 87
6.2.1 持続可能な発電のためのsmrの活用が成長を牽引 87
6.3 101~200MW 88
6.3.1 海水淡水化プラントに必要なエネルギーを供給 88
6.4 201~300MW 89
6.4.1 遠隔地での柔軟性と費用対効果が市場を牽引 89
7 小型モジュール炉市場、冷却材別 91
7.1 導入 92
7.2 重液体金属 93
7.2.1 熱力学的特性が市場成長を支える 93
7.3 水 94
7.3.1 原子炉の超臨界冷却材としての使用がセグメントを押し上げる 94
7.4 溶融塩 95
7.4.1 様々な高温用途への潜在性が成長を促進 95
7.5 ガス 96
7.5.1 ガス冷却炉関連プロセスの効率向上が主要な促進要因 96
8 小型モジュール炉市場、タイプ別 98
8.1 導入 99
8.2 重水炉 101
8.2.1 天然ウランと低濃縮ウランの費用対効果がこの分野を押し上げる 101
8.3 軽水炉 102
8.3.1 技術的即応性と親しみやすさがセグメントを牽引 102
8.3.2 加圧水型原子炉 103
8.3.3 沸騰水型原子炉 104
8.4 高温ガス炉 105
8.4.1 様々な産業用途での使用がセグメントを後押し 105
8.5 高速中性子炉 106
8.5.1 核廃棄物の削減-主要なセグメント牽引要因 106
8.5.2 鉛冷却炉 107
8.5.3 鉛ビスマス炉 107
107 8.5.4 ナトリウム冷却炉
8.6 溶融塩炉 108
8.6.1 核燃料への支出が多い国での採用が成長を牽引 108
9 小型モジュール炉市場、展開別 110
9.1 導入 111
9.2 単一モジュール発電所 112
9.2.1 許認可が比較的容易なことが市場成長を促進 112
9.3 マルチモジュール発電所 113
9.3.1 追加ユニットへの資金調達の容易さがセグメントを牽引 113
10 小型モジュール炉市場(接続性別) 115
10.1 導入 116
10.2 オフグリッド 117
10.2.1 クリーンで柔軟性と信頼性の高い発電へのニーズがセグメントを後押し 117
10.3 グリッド接続 118
10.3.1 自然エネルギーの統合が市場成長を強化 118
11 小型モジュール炉市場:場所別 120
11.1 導入 121
11.2 陸上 122
11.2.1 高い熱効率が市場を牽引 122
11.3 海洋 123
11.3.1 離島、遠隔地、沿岸地域への配備が市場成長を後押し 123
12 小型モジュール炉市場、用途別 125
12.1 導入 126
12.2 発電 127
12.2.1 設置の容易性と運転の柔軟性が需要を牽引 127
12.3 脱塩 128
12.3.1 乾燥・半乾燥地帯における飲料水需要の増加が市場成長を牽引 128
12.4 工業用 129
12.4.1 多様な産業用途へのSMR導入が市場成長を後押し 129
12.4.2 プロセス熱 131
12.4.3 その他 132
12.4.3.1 自家発電 132
12.4.3.2 地域暖房 132
12.5 水素製造 133
12.5.1 負荷率と発電所効率を最大化する能力が市場を牽引 133
13 小型モジュール炉市場、地域別 135
13.1 はじめに 136
13.2 アジア太平洋地域 138
13.2.1 中国 144
13.2.1.1 沿岸部、島嶼部、沖合地域でのSMR配備の増加が市場を牽引 144
13.2.2 日本 145
13.2.2.1 原子力復興への注力とSMRへの投資が市場を後押し 145
13.2.3 インド 146
13.2.3.1 エネルギー容量の増加が原子炉需要を促進 146
13.2.4 韓国 147
13.2.4.1 原子力容量の拡大が市場成長を牽引 147
13.2.5 その他のアジア太平洋地域 148
13.3 アメリカ 149
13.3.1 米国 155
13.3.1.1 投資の増加とデータセンターからのクリーン電力需要の増加が市場を牽引 155
13.3.2 カナダ 156
13.3.2.1 炭素排出削減需要の高まりが有利な成長機会をもたらす 156
13.3.3 アルゼンチン 157
13.3.3.1 発電と海水淡水化用途の需要増加が市場を押し上げる 157
13.4 欧州 158
13.4.1 ロシア 163
13.4.1.1 ロシア極東の遠隔地における発電への展開が市場を牽引 163
13.4.2 イギリス 164
13.4.2.1 政府のイニシアティブと投資の増加が市場成長を促進 164
13.4.3 フランス 165
13.4.3.1 脱炭素目標の達成に向けた取り組みが市場を牽引 165
13.4.4 その他の欧州 166
13.5 中東・アフリカ 167
13.5.1 GCC諸国 173
13.5.1.1 サウジアラビア 173
13.5.1.1.1 発電と海水淡水化のための化石燃料への依存を減らす必要性が市場を牽引 173
13.5.1.2 その他のGCC諸国(定性的) 174
13.5.2 南アフリカ 175
13.5.2.1 第二世代と第三世代技術への関心が需要を押し上げる 175
13.5.3 その他の中東・アフリカ 176
14 競争環境 178
14.1 概要 178
14.1.1 主要企業が採用した戦略(2020~2024年) 178
14.2 市場シェア分析、2023年 179
14.3 市場評価の枠組み 182
14.4 収益分析 183
14.5 企業評価と財務マトリックス 184
14.6 企業評価マトリックス:主要企業、2023年 185
14.6.1 スター企業 185
14.6.2 新興リーダー 185
14.6.3 浸透型プレーヤー 185
14.6.4 参加企業 185
14.6.5 企業フットプリント:主要プレーヤー(2023年) 187
14.6.5.1 製品フットプリント 187
14.6.5.2 市場フットプリント 188
14.6.5.3 地域別フットプリント 189
14.6.5.4 タイプ別フットプリント 190
14.6.5.5 電力容量のフットプリント 191
14.6.5.6 接続性フットプリント 192
14.6.5.7 ロケーションフットプリント 193
14.6.5.8 配置フットプリント 194
14.6.5.9 冷却剤のフットプリント 195
14.6.5.10 アプリケーションフットプリント 196
14.7 企業評価マトリクス:新興企業/SM(2023年) 197
14.7.1 進歩的企業 197
14.7.2 対応力のある企業 197
14.7.3 ダイナミックな企業 197
14.7.4 スタートアップ・ブロック 197
14.7.5 競争ベンチマーキング(新興企業/SM)(2023年) 199
14.7.5.1 主要新興企業/中小企業のリスト 199
14.7.5.2 主要新興企業の競争ベンチマーク 200
14.7.5.3 主要新興企業の競合ベンチマーキング 201
14.8 競争シナリオと動向 202
14.8.1 取引 202
14.8.2 拡張 203
14.9 ブランド/製品の比較 204
15 会社プロファイル 205
State Atomic Energy Corporation Rosatom (Russia)
China National Nuclear Corporation (China)
Westinghouse Electric Company LLC (US)
MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES LTD. (Japan)
GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (US)
16 付録 283
16.1 業界専門家の洞察 283
16.2 ディスカッションガイド 284
16.3 Knowledgestore: Marketsandmarketsの購読ポータル 289
16.4 カスタマイズオプション 291
16.5 関連レポート 291
16.6 著者の詳細 292
The superiority of the small modular reactors in relation to their modular size and safety features spearheads the growth of the small modular reactor market. Modularity enables simpler deployment in any location, ranging from remote ones to areas lacking infrastructure. Moreover, the current environmental policies and incentives on carbon dioxide emission reduction further the push the SMRs to compete with fossil fuel power plants.
“Water, by coolant, is expected to be the largest segment from 2024 to 2030.”
The water segment is expected to largest segment in the small modular reactors market. Using water as a coolant in ordinary conditions can greatly affect nuclear fission because it absorbs fast-moving neutrons. Advancements in the reactors for the proper handling of the water coolants have brought in new technologies such as super-critical water reactors, which have increased the thermal efficiency of the water-cooled reactors. These developments are expected to fuel the water coolant market.
“Land, by location, is expected to be the largest and fastest-growing market from 2024 to 2030”
It is expected that the land segment in the small modular reactors market will grow at a faster rate. Land SMRs utilize various reactor technology configurations, such as light-water reactors, heavy-water reactors, molten salt reactors, high-temperature gas-cooled reactors, and fast-neutron reactors, for grid connection and off-grid applications. Land SMRs have higher thermal efficiency compared with marine or naval SMRs. The potential for underground deployment of land reactor units provides various advantages, such as enhanced protection from natural hazards (earthquakes, flooding, tsunami, etc.) and disasters such as the impact of an aircraft crash.
“Asia Pacific is expected be the largest market for small modular reactors.”
Asia Pacific is going to witness the largest market share for the small modular reactors. The Asia Pacific region is a key driver of the small modular reactors (SMRs) market, fueled by a combination of rapid industrialization, increasing energy demand, and a strong commitment to reducing carbon emissions. These growing investments drive the growth of the SMR. Also, the countries like China, and Russia are coming up with major projects which are going to be operational by 2030.
In-depth interviews have been conducted with chief executive officers (CEOs), Directors, and other executives from various key organizations operating in the small modular reactor market.
By Company Type: Tier 1- 60%, Tier 2- 25%, and Tier 3- 15%
By Designation: C-level Executives - 35%, Director Level- 25%, and Others- 40%
By Region: Americas – 30%, Europe – 25%, Asia Pacific – 30%, Middle East & Africa – 15%
Note: Other designations include sales managers, marketing managers, product managers, and product engineers.
The tier of the companies is defined based on their total revenue as of 2023. Tier 1: USD 1 billion and above, Tier 2: From USD 500 million to USD 1 billion, and Tier 3:
The small modular reactor market is dominated by a few major players that have a wide regional presence. The leading players in the small modular reactor market are State Atomic Energy Corporation Rosatom (Russia), China National Nuclear Corporation (China), Westinghouse Electric Company LLC (US), MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD. (Japan), GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (US) among others. The major strategy adopted by the players includes agreements, partnership, memorandum of understanding, acquisitions, and expansions.
Research Coverage:
The report defines, describes, and forecasts the small modular reactor market by type, connectivity, deployment, power rating, location, application, coolant, and region. It also offers a detailed qualitative and quantitative analysis of the market. The report comprehensively reviews the major market drivers, restraints, opportunities, and challenges. It also covers various important aspects of the market. A detailed analysis of the key industry players has been done to provide insights into their business overview, solutions, and services; key strategies; Contracts, partnerships, agreements, memorandum of understanding, and recent developments associated with the small modular reactor market. Competitive analysis of upcoming startups in the small modular reactor market ecosystem is covered in this report.
Reasons to buy this report:
Reasons to buy this report The report will help the market leaders/new entrants market and the subsegments. This report will help stakeholders understand the competitive landscape and gain more insights to position their businesses better and to plan suitable go-to-market strategies. The report also helps stakeholders understand the pulse of the market and provides them with information on key market drivers, restraints, challenges, and opportunities.
The report provides insights on the following pointers:
•Analysis of key drivers (growing focus on decarbonizing economies to align with net zero emission goals, modular nature and factory construction of small modular reactors offers cost effectiveness and growing investments in SMR technology are just a few of the primary drivers propelling the small modular reactor market), restraints (stringent regulatory policies and standards and negative public perception of nuclear power technology, limit the market's expansion), opportunities (Minimizing the risk associated with nuclear operations and growing demand for clean power in the data centers), and challenges (Lack of standard licensing process) influencing the growth.
•Product Development/ Innovation: The small modular reactor market is seeing substantial product development and innovation, driven by need for decarbonization. Companies are investing in various SMR technologies.
•Market Development: In June 2022, Rolls-Royce plc announced to open its new head office in central Manchester to support its expansion and the deployment of Small Modular Reactors, aiming to recruit 850 staff by year-end. CEO Tom Samson emphasized the city's historical significance for the company, while Business Secretary Kwasi Kwarteng welcomed the move.
•Market Diversification: On october 2024, Google signed a deal with Kairos Power to buy clean power to meet its data centers demand.
•Competitive Assessment: In-depth analysis of market share, growth plans, and service offerings of top companies in the small modular reactor market, including State Atomic Energy Corporation Rosatom (Russia), China National Nuclear Corporation (China), Westinghouse Electric Company LLC (US), MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD. (Japan), GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (US) among others.
1 INTRODUCTION 27
1.1 STUDY OBJECTIVES 27
1.2 MARKET DEFINITION 27
1.3 STUDY SCOPE 28
1.3.1 INCLUSIONS AND EXCLUSIONS 28
1.3.2 MARKETS COVERED AND REGIONAL SCOPE 29
1.3.3 YEARS CONSIDERED 30
1.4 CURRENCY CONSIDERED 30
1.5 UNIT CONSIDERED 30
1.6 RESEARCH LIMITATIONS 30
1.7 STAKEHOLDERS 31
1.8 SUMMARY OF CHANGES 31
2 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY 32
2.1 RESEARCH DATA 32
2.2 PRIMARY AND SECONDARY RESEARCH 33
2.2.1 SECONDARY DATA 33
2.2.2 KEY DATA FROM SECONDARY SOURCES 33
2.2.3 PRIMARY DATA 34
2.2.3.1 Key data from primary sources 34
2.2.3.2 Breakdown of primaries 35
2.3 MARKET SIZE ESTIMATION 36
2.3.1 BOTTOM-UP APPROACH 36
2.3.2 TOP-DOWN APPROACH 37
2.3.3 DEMAND-SIDE ANALYSIS 38
2.3.3.1 Assumptions for demand-side analysis 38
2.3.3.2 Calculations for demand-side analysis 39
2.3.4 SUPPLY-SIDE ANALYSIS 39
2.3.4.1 Calculations for supply-side analysis 40
2.3.4.2 Assumptions for supply-side analysis 40
2.4 MARKET BREAKDOWN AND DATA TRIANGULATION 41
2.5 FORECAST 41
2.6 RISK ASSESSMENT 42
3 EXECUTIVE SUMMARY 43
4 PREMIUM INSIGHTS 49
4.1 ATTRACTIVE OPPORTUNITIES FOR PLAYERS IN SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET 49
4.2 SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET, BY REGION 50
4.3 SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET, BY COOLANT 50
4.4 SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET, BY TYPE 51
4.5 SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET, BY CONNECTIVITY 51
4.6 SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT 51
4.7 SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET, BY LOCATION 52
4.8 SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET, BY APPLICATION 52
4.9 SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET, BY POWER RATING 52
4.10 SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET IN ASIA PACIFIC, BY TYPE AND COUNTRY 53
5 MARKET OVERVIEW 54
5.1 INTRODUCTION 54
5.2 MARKET DYNAMICS 54
5.2.1 DRIVERS 55
5.2.1.1 Growing focus on decarbonization to align with net zero emission goals 55
5.2.1.2 Cost-effectiveness and scalability due to modular nature and factory construction 56
5.2.1.3 Growing investments in SMR technology 56
5.2.2 RESTRAINTS 56
5.2.2.1 Stringent regulatory policies and standards 56
5.2.2.2 Negative public perception of nuclear power technology 57
5.2.3 OPPORTUNITIES 57
5.2.3.1 Minimizing risk associated with nuclear operations 57
5.2.3.2 Integration of SMRs with renewable energy sources 58
5.2.4 CHALLENGES 59
5.2.4.1 Lack of standard licensing process 59
5.3 TRENDS/DISRUPTIONS IMPACTING CUSTOMER BUSINESS 59
5.4 SUPPLY CHAIN ANALYSIS 60
5.5 ECOSYSTEM ANALYSIS 61
5.6 INVESTMENT FROM DATA CENTERS/AI COMPANIES IN SMR/NUCLEAR ENERGY 62
5.7 TECHNOLOGY ANALYSIS 62
5.7.1 KEY TECHNOLOGIES 62
5.7.1.1 Nuclear Fission 62
5.7.1.2 Light Water Reactors 62
5.7.1.3 Heavy Water Reactors 62
5.7.1.4 Fast Neutron Reactors 63
5.7.1.5 Molten Salt Reactors 63
5.7.2 COMPLEMENTARY TECHNOLOGIES 63
5.7.2.1 Integration of Renewable Energy 63
5.7.2.2 Smart Grid Integration 63
5.7.3 ADJACENT TECHNOLOGIES 64
5.7.3.1 Hydrogen Production 64
5.8 CASE STUDY ANALYSIS 64
5.8.1 FINNISH GOVERNMENT ENACTS LAW FOR ALTERNATIVE SYSTEMS TO REDUCE CARBON EMISSIONS 64
5.8.2 NUSCALE POWER, LLC RECEIVES DESIGN APPROVAL FOR VOYGR DEPLOYMENT AT IDAHO NATIONAL LABORATORY TO MEET CLEAN ENERGY GOALS 64
5.8.3 SCAFFOLDING SOLUTIONS HELPS SOUTH CAROLINA NUCLEAR POWER PLANT WITH MONITORING, INSPECTION, AND MAINTENANCE 65
5.9 PATENT ANALYSIS 66
5.10 PRICING ANALYSIS 68
5.10.1 AVERAGE PRICING TREND, BY TYPE 68
5.10.2 PRICING TREND, BY REGION 69
5.11 TRADE ANALYSIS 69
5.11.1 IMPORT SCENARIO 69
5.11.2 EXPORT SCENARIO 70
5.12 KEY CONFERENCES AND EVENTS, 2024–2025 71
5.13 REGULATORY LANDSCAPE 72
5.13.1 REGULATORY BODIES, GOVERNMENT AGENCIES, AND OTHER ORGANIZATIONS 72
5.13.2 REGULATORY FRAMEWORKS/POLICIES 75
5.13.2.1 Regulatory frameworks/policies in Americas 75
5.13.2.2 Regulatory frameworks/policies in Asia Pacific 76
5.13.2.3 Regulatory frameworks/policies in Europe 76
5.14 PORTER'S FIVE FORCES ANALYSIS 77
5.14.1 THREAT OF SUBSTITUTES 78
5.14.2 BARGAINING POWER OF SUPPLIERS 78
5.14.3 BARGAINING POWER OF BUYERS 78
5.14.4 THREAT OF NEW ENTRANTS 79
5.14.5 INTENSITY OF COMPETITIVE RIVALRY 79
5.15 KEY STAKEHOLDERS AND BUYING CRITERIA 79
5.15.1 KEY STAKEHOLDERS IN BUYING PROCESS 79
5.15.2 BUYING CRITERIA 80
5.16 INVESTMENT AND FUNDING SCENARIO 81
5.17 IMPACT OF GENERATIVE AI IN SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET 81
5.17.1 ADOPTION OF GENERATIVE AI APPLICATIONS IN SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET 81
5.17.2 IMPACT OF GENERATIVE AI, BY APPLICATION 82
5.17.3 IMPACT OF GENERATIVE AI ON SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET, BY REGION 82
5.18 MACROECONOMIC OUTLOOK FOR SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET 83
6 SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET, BY POWER RATING 85
6.1 INTRODUCTION 86
6.2 UP TO 100 MW 87
6.2.1 HARNESSING SMR FOR SUSTAINABLE ELECTRICITY GENERATION TO DRIVE GROWTH 87
6.3 101–200 MW 88
6.3.1 PROVIDES NECESSARY ENERGY FOR DESALINATION PLANTS 88
6.4 201–300 MW 89
6.4.1 FLEXIBILITY IN REMOTE AREAS AND COST-EFFECTIVENESS TO DRIVE MARKET 89
7 SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET, BY COOLANT 91
7.1 INTRODUCTION 92
7.2 HEAVY LIQUID METALS 93
7.2.1 THERMODYNAMIC PROPERTIES TO SUPPORT MARKET GROWTH 93
7.3 WATER 94
7.3.1 USE AS SUPER-CRITICAL COOLANT IN REACTORS TO BOOST SEGMENT 94
7.4 MOLTEN SALTS 95
7.4.1 POTENTIAL TO SERVE VARIED HIGH-TEMPERATURE APPLICATIONS TO FUEL GROWTH 95
7.5 GASES 96
7.5.1 IMPROVED EFFICIENCY IN GAS-COOLED REACTOR-RELATED PROCESSES – KEY DRIVER 96
8 SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET, BY TYPE 98
8.1 INTRODUCTION 99
8.2 HEAVY WATER REACTORS 101
8.2.1 COST-EFFECTIVENESS OF NATURAL AND LOW-ENRICHED URANIUM TO BOOST SEGMENT 101
8.3 LIGHT WATER REACTORS 102
8.3.1 TECHNOLOGICAL READINESS AND FAMILIARITY TO DRIVE SEGMENT 102
8.3.2 PRESSURIZED WATER REACTORS 103
8.3.3 BOILING WATER REACTORS 104
8.4 HIGH-TEMPERATURE REACTORS 105
8.4.1 USE IN VARIOUS INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS TO BOOST SEGMENT 105
8.5 FAST NEUTRON REACTORS 106
8.5.1 REDUCTION IN NUCLEAR WASTE – KEY SEGMENT DRIVER 106
8.5.2 LEAD-COOLED REACTORS 107
8.5.3 LEAD-BISMUTH REACTORS 107
8.5.4 SODIUM-COOLED REACTORS 107
8.6 MOLTEN SALT REACTORS 108
8.6.1 ADOPTION BY COUNTRIES WITH HIGH SPENDING ON NUCLEAR FUEL TO DRIVE GROWTH 108
9 SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET, BY DEPLOYMENT 110
9.1 INTRODUCTION 111
9.2 SINGLE-MODULE POWER PLANTS 112
9.2.1 RELATIVE EASE OF LICENSING TO DRIVE MARKET GROWTH 112
9.3 MULTI-MODULE POWER PLANTS 113
9.3.1 EASE OF FINANCING ADDITIONAL UNITS TO DRIVE SEGMENT 113
10 SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET, BY CONNECTIVITY 115
10.1 INTRODUCTION 116
10.2 OFF-GRID 117
10.2.1 NEED FOR CLEAN, FLEXIBLE, AND RELIABLE POWER GENERATION TO BOOST SEGMENT 117
10.3 GRID-CONNECTED 118
10.3.1 INTEGRATION OF RENEWABLES TO STRENGTHEN MARKET GROWTH 118
11 SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET, BY LOCATION 120
11.1 INTRODUCTION 121
11.2 LAND 122
11.2.1 HIGHER THERMAL EFFICIENCY TO DRIVE MARKET 122
11.3 MARINE 123
11.3.1 DEPLOYMENT IN ISLANDS, REMOTE, AND COASTAL REGIONS TO BOOST MARKET GROWTH 123
12 SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET, BY APPLICATION 125
12.1 INTRODUCTION 126
12.2 POWER GENERATION 127
12.2.1 EASE OF SITING AND OPERATING FLEXIBILITY TO DRIVE DEMAND 127
12.3 DESALINATION 128
12.3.1 INCREASING DEMAND FOR POTABLE WATER IN ARID AND SEMI-ARID ZONES TO DRIVE MARKET GROWTH 128
12.4 INDUSTRIAL 129
12.4.1 ANTICIPATED DEPLOYMENT OF SMR IN DIVERSE INDUSTRIAL APPLICATIONS TO BOOST MARKET GROWTH 129
12.4.2 PROCESS HEAT 131
12.4.3 OTHERS 132
12.4.3.1 Captive electricity generation 132
12.4.3.2 District heating 132
12.5 HYDROGEN PRODUCTION 133
12.5.1 ABILITY TO MAXIMIZE LOAD FACTORS AND POWER PLANT EFFICIENCY TO DRIVE MARKET 133
13 SMALL MODULAR REACTORS MARKET, BY REGION 135
13.1 INTRODUCTION 136
13.2 ASIA PACIFIC 138
13.2.1 CHINA 144
13.2.1.1 Rise in deployment of SMRs in coastal, island, and offshore areas to drive market 144
13.2.2 JAPAN 145
13.2.2.1 Focus on nuclear recovery and investments in SMR to fuel market 145
13.2.3 INDIA 146
13.2.3.1 Advancements in energy capacity to drive demand for reactors 146
13.2.4 SOUTH KOREA 147
13.2.4.1 Expansion of nuclear energy capacity to drive market growth 147
13.2.5 REST OF ASIA PACIFIC 148
13.3 AMERICAS 149
13.3.1 US 155
13.3.1.1 Rising investments and growing demand for clean power from data centers to drive market 155
13.3.2 CANADA 156
13.3.2.1 Growing demand for reduction in carbon emissions to provide lucrative growth opportunities 156
13.3.3 ARGENTINA 157
13.3.3.1 Rising demand for power generation and desalination applications to boost market 157
13.4 EUROPE 158
13.4.1 RUSSIA 163
13.4.1.1 Deployment for power generation in remote areas of Russian Far East to drive market 163
13.4.2 UK 164
13.4.2.1 Increasing government initiatives and investments to fuel market growth 164
13.4.3 FRANCE 165
13.4.3.1 Focus on achieving decarbonization target to drive market 165
13.4.4 REST OF EUROPE 166
13.5 MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA 167
13.5.1 GCC COUNTRIES 173
13.5.1.1 Saudi Arabia 173
13.5.1.1.1 Need to reduce dependence on fossil fuels for power generation and desalination to drive market 173
13.5.1.2 Other GCC Countries (Qualitative) 174
13.5.2 SOUTH AFRICA 175
13.5.2.1 Interest in Generation II and III technologies to boost demand 175
13.5.3 REST OF MIDDLE EAST & AFRICA 176
14 COMPETITIVE LANDSCAPE 178
14.1 OVERVIEW 178
14.1.1 STRATEGIES ADOPTED BY KEY PLAYERS, 2020–2024 178
14.2 MARKET SHARE ANALYSIS, 2023 179
14.3 MARKET EVALUATION FRAMEWORK 182
14.4 REVENUE ANALYSIS 183
14.5 COMPANY VALUATION AND FINANCIAL MATRIX 184
14.6 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: KEY PLAYERS, 2023 185
14.6.1 STARS 185
14.6.2 EMERGING LEADERS 185
14.6.3 PERVASIVE PLAYERS 185
14.6.4 PARTICIPANTS 185
14.6.5 COMPANY FOOTPRINT: KEY PLAYERS, 2023 187
14.6.5.1 Product footprint 187
14.6.5.2 Market footprint 188
14.6.5.3 Regional footprint 189
14.6.5.4 Type footprint 190
14.6.5.5 Power capacity footprint 191
14.6.5.6 Connectivity footprint 192
14.6.5.7 Location footprint 193
14.6.5.8 Deployment footprint 194
14.6.5.9 Coolant footprint 195
14.6.5.10 Application footprint 196
14.7 COMPANY EVALUATION MATRIX: STARTUPS/SMES, 2023 197
14.7.1 PROGRESSIVE COMPANIES 197
14.7.2 RESPONSIVE COMPANIES 197
14.7.3 DYNAMIC COMPANIES 197
14.7.4 STARTING BLOCKS 197
14.7.5 COMPETITIVE BENCHMARKING, STARTUPS/SMES, 2023 199
14.7.5.1 List of key startups/SMEs 199
14.7.5.2 Competitive benchmarking of key startups/SMEs 200
14.7.5.3 Competitive benchmarking of key startups/SMEs 201
14.8 COMPETITIVE SCENARIO AND TRENDS 202
14.8.1 DEALS 202
14.8.2 EXPANSIONS 203
14.9 BRAND/PRODUCT COMPARISON 204
15 COMPANY PROFILES 205
15.1 KEY PLAYERS 205
15.1.1 THE STATE ATOMIC ENERGY CORPORATION ROSATOM 205
15.1.1.1 Business overview 205
15.1.1.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered 206
15.1.1.3 Recent developments 207
15.1.1.3.1 Deals 207
15.1.1.4 MnM view 208
15.1.1.4.1 Right to win 208
15.1.1.4.2 Strategic choices 208
15.1.1.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats 208
15.1.2 CHINA NATIONAL NUCLEAR CORPORATION 209
15.1.2.1 Business overview 209
15.1.2.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered 209
15.1.2.3 Recent developments 210
15.1.2.3.1 Deals 210
15.1.2.3.2 Other developments 211
15.1.2.4 MnM view 211
15.1.2.4.1 Right to win 211
15.1.2.4.2 Strategic choices 211
15.1.2.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats 211
15.1.3 WESTINGHOUSE ELECTRIC COMPANY LLC 212
15.1.3.1 Business overview 212
15.1.3.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered 212
15.1.3.3 Recent developments 213
15.1.3.3.1 Deals 213
15.1.3.3.2 Expansions 215
15.1.3.3.3 Other developments 217
15.1.3.4 MnM view 218
15.1.3.4.1 Right to win 218
15.1.3.4.2 Strategic choices 218
15.1.3.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats 218
15.1.4 GE HITACHI NUCLEAR ENERGY 219
15.1.4.1 Business overview 219
15.1.4.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered 219
15.1.4.3 Recent developments 220
15.1.4.3.1 Deals 220
15.1.4.3.2 Expansions 222
15.1.4.3.3 Other developments 222
15.1.4.4 MnM view 222
15.1.4.4.1 Right to win 222
15.1.4.4.2 Strategic choices 222
15.1.4.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats 223
15.1.5 MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES, LTD. 224
15.1.5.1 Business overview 224
15.1.5.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered 225
15.1.5.3 Recent developments 226
15.1.5.3.1 Deals 226
15.1.5.4 MnM view 226
15.1.5.4.1 Right to win 226
15.1.5.4.2 Strategic choices 227
15.1.5.4.3 Weaknesses and competitive threats 227
15.1.6 ROLLS-ROYCE PLC 228
15.1.6.1 Business overview 228
15.1.6.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered 229
15.1.6.3 Recent developments 230
15.1.6.3.1 Deals 230
15.1.6.3.2 Expansions 233
15.1.7 ATKINSRÉALIS 234
15.1.7.1 Business overview 234
15.1.7.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered 235
15.1.7.3 Recent developments 236
15.1.7.3.1 Deals 236
15.1.8 NUSCALE POWER, LLC. 238
15.1.8.1 Business overview 238
15.1.8.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered 239
15.1.8.3 Recent developments 239
15.1.8.3.1 Deals 239
15.1.8.3.2 Expansions 245
15.1.8.3.3 Other developments 246
15.1.9 ULTRA SAFE NUCLEAR 247
15.1.9.1 Business overview 247
15.1.9.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered 247
15.1.9.3 Recent developments 248
15.1.9.3.1 Deals 248
15.1.9.3.2 Expansions 250
15.1.10 TERRESTRIAL ENERGY INC. 251
15.1.10.1 Business overview 251
15.1.10.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered 251
15.1.10.3 Recent developments 252
15.1.10.3.1 Deals 252
15.1.10.3.2 Expansions 254
15.1.10.3.3 Other developments 255
15.1.11 MOLTEX ENERGY 256
15.1.11.1 Business overview 256
15.1.11.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered 256
15.1.11.3 Recent developments 257
15.1.11.3.1 Deals 257
15.1.11.3.2 Other developments 258
15.1.12 X-ENERGY, LLC. 259
15.1.12.1 Business overview 259
15.1.12.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered 259
15.1.12.3 Recent developments 260
15.1.12.3.1 Deals 260
15.1.12.3.2 Other developments 263
15.1.13 HOLTEC INTERNATIONAL 264
15.1.13.1 Business overview 264
15.1.13.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered 264
15.1.13.3 Recent developments 265
15.1.13.3.1 Deals 265
15.1.13.3.2 Expansions 267
15.1.13.3.3 Other developments 267
15.1.14 GENERAL ATOMICS 269
15.1.14.1 Business overview 269
15.1.14.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered 269
15.1.14.3 Recent developments 270
15.1.14.3.1 Deals 270
15.1.14.3.2 Other developments 271
15.1.15 KEPCO ENGINEERING & CONSTRUCTION COMPANY.INC 272
15.1.15.1 Business overview 272
15.1.15.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered 273
15.1.15.3 Recent developments 273
15.1.15.3.1 Deals 273
15.1.16 TOSHIBA ENERGY SYSTEMS & SOLUTIONS CORPORATION 275
15.1.16.1 Business overview 275
15.1.16.2 Products/Solutions/Services offered 275
15.1.16.3 Recent developments 276
15.1.16.3.1 Deals 276
15.2 OTHER PLAYERS 277
15.2.1 BLYKALLA 277
15.2.2 KAIROS POWER LLC 278
15.2.3 FRAMATOME 278
15.2.4 ARC CLEAN TECHNOLOGY, INC 279
15.2.5 SEABORG TECHNOLOGIES 279
15.2.6 TOKAMAK ENERGY LTD. 280
15.2.7 TERRAPOWER LLC 280
15.2.8 FLIBE ENERGY, INC. 281
15.2.9 OKLO INC. 281
15.2.10 COPENHAGEN ATOMICS 282
16 APPENDIX 283
16.1 INSIGHTS OF INDUSTRY EXPERTS 283
16.2 DISCUSSION GUIDE 284
16.3 KNOWLEDGESTORE: MARKETSANDMARKETS’ SUBSCRIPTION PORTAL 289
16.4 CUSTOMIZATION OPTIONS 291
16.5 RELATED REPORTS 291
16.6 AUTHOR DETAILS 292
❖ 世界の小型モジュール炉市場に関するよくある質問(FAQ) ❖
・小型モジュール炉の世界市場規模は?
→MarketsandMarkets社は2024年の小型モジュール炉の世界市場規模を60億米ドルと推定しています。
・小型モジュール炉の世界市場予測は?
→MarketsandMarkets社は2030年の小型モジュール炉の世界市場規模を71.4億米ドルと予測しています。
・小型モジュール炉市場の成長率は?
→MarketsandMarkets社は小型モジュール炉の世界市場が2024年~2030年に年平均3.0%成長すると予測しています。
・世界の小型モジュール炉市場における主要企業は?
→MarketsandMarkets社は「State Atomic Energy Corporation Rosatom (Russia)、China National Nuclear Corporation (China)、Westinghouse Electric Company LLC (US)、MITSUBISHI HEAVY INDUSTRIES、LTD. (Japan)、GE Hitachi Nuclear Energy (US)など ...」をグローバル小型モジュール炉市場の主要企業として認識しています。
※上記FAQの市場規模、市場予測、成長率、主要企業に関する情報は本レポートの概要を作成した時点での情報であり、納品レポートの情報と少し異なる場合があります。